Customer Experience Journey Mapping Strategies to Improve Business Performance
Customer experience journey mapping is how organizations visualize the end-to-end customer experience. Effective customer journey maps result in improved customer experience and business performance.
Did you know that 77% of organizations cannot consistently create a consistent customer experience across channels? This often stems from poor internal communication, outdated technology, or inefficient processes.
However, to combat this, you need to understand the end-to-end customer experience and be prepared for every path a consumer might take to become a customer or that a current customer might take when using your products or services.
Whether you are looking to change current processes, improve old ones, or ensure that your team is aligned on the priorities of the customer experience, creating a customer journey map will be useful to your organization.
What is Customer Journey Mapping?
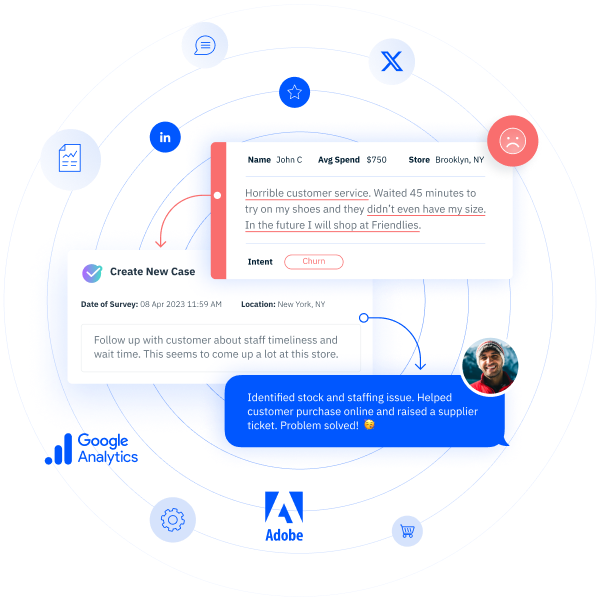
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the journey a customer has with a company’s brand, products, services, and people. Customer journey maps may also be called customer interaction maps, customer corridors, or service blueprints.
A customer journey map visualizes all touch points between the customer and the organization, from customer research on the product to first contact with the company to building customer loyalty.

By constructing theoretical customer decision-making scenarios, companies can more easily understand the factors and product features influencing customers’ purchase decisions. With InMoment’s XI Platform, you can create a customer journey map that tracks the customer journey across different channels and gives you insight on how to optimize it.
The Benefits of Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping allows companies to see the gaps between the desired customer experience and the one the customer receives. Creating a customer journey map can help organizations improve:
- Internal education and alignment
- Resource allocation
- Product lines
- Processes
- Customer Experience
Improved Internal Education & Alignment
Over 81% of CX practitioners agreed that customer experience journey mapping was successful at internally educating stakeholders about consumer pain points or unmet needs. This can be useful to show employees that one problem or mistake in one phase of the customer journey can hurt the customer’s overall experience.
Furthermore, customer journey maps educate stakeholders and get them on the same page about what is most important. Almost 80% of employees who created a customer journey map at their organization say it helped generate alignment between internal teams.
Increased Resource Allocation
Customer journey maps can help you identify problems and present a strong business case for customer experience improvement. 71% of organizations say customer journey mapping has successfully persuaded management to invest in CX efforts and fix existing customer problems.
Improved Product Lines
Customer experience journey mapping identifies where you may be failing in the customer experience and gives you room to improve. Problems identified through customer journey mapping could be a confusing website navigation bar or a checkout process with too many steps.
With this information, you can improve your customer experience and eliminate pain points. In fact, over 70% of organizations say that customer journey mapping has helped them improve the user experience (UX) of a product or service or has helped them gain investment to create new features.
Improved Processes
Most professionals using customer journey maps agree that one of their benefits is identifying the need for internal optimizations. By visualizing the customer’s experience across various touchpoints, journey maps provide a clearer understanding of where internal processes may be causing delays, confusion, or frustration for both customers and employees.
Whether it’s a lack of cross-departmental communication, inefficient workflows, or outdated technology, journey maps can expose these pain points and allow organizations to align their internal operations more effectively to improve overall efficiency.
Improved Customer Experience
All of these benefits connect to creating a customer experience that consistently meets or exceeds customer expectations. Almost 90% of customer experience professionals who use customer journey mapping report improved performance in customer experience KPIs such as
higher customer satisfaction, lower customer churn, and improved Net Promoter Score.
Why Customer Journey Mapping is Important
Creating a customer journey map is important because it helps visualize the customer journey. Improving the entire customer experience can be difficult when only focusing on one stage or aspect.
Seeing all the touchpoints together, how they relate to each other, and how they help the customer move through the journey helps your organization understand how each piece of the customer experience puzzle fits together.
5 Types of Customer Journey Maps
There are different types of journey maps for different use cases. Each is tailored to specific goals and stages of the customer experience. Different journey maps provide unique insights, whether you’re looking to understand how customers interact with your brand today, envision an ideal future state, or analyze internal processes that affect customer outcomes. Here are some of the most common types of customer journey maps and when to use them:
Buyer’s Journey
- Purpose: To map out the process a potential customer goes through before making a purchase decision and becoming a customer. This type of journey map helps you understand what motivates a consumer at each stage, their questions, and the information they seek.
- When to Use: This journey map is used when developing marketing and sales strategies that aim to guide prospective customers through their decision-making process. It is particularly useful for aligning teams across multiple departments, such as marketing, sales, and customer success.
- Focus: This journey map focuses on the buyer’s thought process, motivations, pain points, and needs at each stage of the journey. It typically covers awareness, consideration, and decision.
- Example: A SaaS company creates a buyer’s journey map to understand how potential customers discover their product, research competitors, and make decisions. The map helps the company tailor content to each stage, such as blog posts and webinars for the awareness stage, product comparisons during the consideration stage, and free trials or demos for the decision stage.
Current State
- Purpose: This map reflects the existing customer experience based on how customers interact with your products or services today. It is useful for diagnosing current inefficiencies and identifying areas for improvement.
- When to Use: When you want to understand what is happening now, spot bottlenecks or optimize current processes.
- Focus: Real-time customer journey analytics to understand the emotions, pain points, and touchpoints customers are experiencing at every stage.
- Example: A retail company maps out how a customer currently shops on its e-commerce platform and identifies the complex checkout process as an area of improvement to improve the e-commerce customer experience.
Future State
- Purpose: The future state journey map outlines the ideal customer experience you want to create. It will look different from a current state journey map because it shows how interactions could be improved.
- When to use: This journey map is most useful when redesigning or improving current processes.
- Focus: Future state journey maps focus on optimizing processes, streamlining interactions, and improving customers’ emotional states at each stage.
- Example: A software company wanting to overhaul their customer support process to improve resolution times can create a future state journey map to show what the ideal process would look like.
Day-in-the-Life
- Purpose: The day-in-the-life customer journey map takes a broader view of the customer’s life beyond their interactions with your brand. It focuses on the typical day for the customer and how your product or service fits into their life.
- When to Use: This can help you better understand your customers and identify better ways to serve them.
- Focus: Day-in-the-life customer journey maps focus on customer activities, goals, frustrations, and needs within their daily routine and how that intersects with your product or service.
- Example: A fitness app company maps out the day in the life of a busy working parent to see how and when the app could help them achieve their fitness goals in their busy schedule.
Service Blueprint
- Purpose: The service blueprint journey map extends beyond the customer journey and includes business processes and systems that enable the customer experience that aren’t usually showcased in other journey maps. It visualizes the connections between the front-stage (customer-facing) and back-stage (internal processes).
- When to Use: This can be used to improve internal processes that impact the customer experience or to optimize service delivery systems.
- Focus: Service blueprints showcase the customer journey and the underlying business activities with equal importance.
- Example: A provider working to improve customer experience in healthcare maps out the patient’s journey, internal systems, staff interactions, and other elements needed to deliver a quality healthcare customer experience.
How to Create A Customer Journey Map
Creating a customer journey map is an important process that should not be taken lightly. When building your customer journey map, it is important to follow the right steps to produce the most accurate and effective map for your organization.
When you partner with InMoment, you get access to customer experience consulting with practitioners with over 50 years of combined experience that can help you build the best customer experience journey map for your organization.
However, if you are not using those services, here is an overview of how to create a customer journey map from scratch:
Step 1: Outline Your Objectives
Why do you want to create a customer experience journey map? Are you trying to improve a specific touchpoint, understand customer pain points, or increase the lead-to-customer conversion rate? Creating a customer journey map is a detailed process that often involves collaboration from multiple departments, so outlining what you hope to learn as a result of the customer journey map will make sure the efforts are well spent.
Step 2: Create Customer Personas
Next, you will want to develop detailed customer personas that represent different segments of your customer base. You might have already created these as part of your customer experience strategy. These personas should include important customer information such as demographics, needs, behaviors, goals, and challenges.
Step 3: Map Out the Stages of the Customer Journey
This is one of the most important steps in creating an effective customer journey map. You will outline the stages and touchpoints customers will experience in this stage. Typical stages of the customer journey include awareness, consideration, and purchase. Some business models might include retention and advocacy after the purchase stage.
Touchpoints refer to the places where your customers interact with your business. These could include the website, customer support portal, social media, and more. Outlining the high-level view of the customer journey will make it easier to examine specific sections of your …
Step 4: Identify Customer Goals and Actions
You need to identify what the customer is trying to achieve at each stage of the customer journey. For example, in the awareness stage, they may be trying to gather information and create a shortlist. In the consideration stage, they want to see what product or service makes the most sense.
Once you have identified these goals, outline the steps the customer will take to meet those goals, such as conducting online searches, reading customer reviews, or contacting your team directly. When you have the goals and actions outlined, you can position your organization to be prepared to meet customer needs.
Step 5: Understand Customer Sentiment
While customer sentiment is usually a metric reserved for consumers who have already become customers, it can be useful in creating a customer journey map. Customer sentiment is how a customer feels about a brand’s products or services. It can be useful in customer journey mapping to see how customers feel about your brand at every stage of their journey.
For example, suppose you discover that consumers didn’t like the email they received after downloading a document from your website. In that case, you can remove or change the email to prevent further customers from abandoning their journey.
InMoment’s XI Platform makes sentiment analysis easy with best-in-class natural language processing (NLP) that categorizes, sorts and tracks customer sentiment.
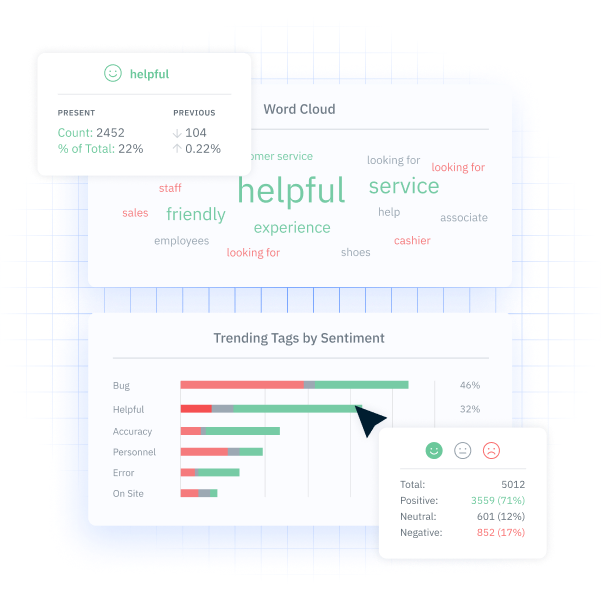
Step 6: Visualize the Journey Map
Once you have completed all these steps, you can visualize the customer journey map. Create a visual representation of the journey using a customer journey map template. Your journey map should clearly show the stages, touchpoints, goals, emotions, and pain points a customer might experience.
Step 7: Gather Internal Feedback
After putting it all together in a visual form, share the journey map with internal teams not involved in the customer journey mapping process. You can even share it with existing loyal customers. Sharing the customer journey map in these groups will help you verify its accuracy and identify anything that needs to be fixed.
Step 8: Track Customer Journeys
Once your map is complete, tracking real customer journeys is essential to see how they align with your assumptions. Use analytics tools, customer feedback, and data from CRM systems to monitor how customers interact with your brand across touchpoints.
By tracking these journeys, you can identify patterns, measure the success of any implemented changes, and spot potential gaps in the customer experience that may not have been visible in the initial mapping process.
Step 9: Use the Customer Journey Map to Drive Action
A customer journey map is only as good as the insights that come from it. Use your customer experience journey mapping to help inform your strategies and initiatives across departments.
For example, you may notice that customers are more likely to convert when they receive a discount on their first purchase or that a specific landing page in a campaign has a bounce rate. These metrics can help you drive transformative action within your organization.
Step 10: Share Wins
Once you start seeing the impact of your customer journey improvements, it’s important to celebrate and share these successes. Sharing results reinforces the value of journey mapping and motivates continued investment in customer experience initiatives. Document these improvements so they can serve as benchmarks for future efforts and inspire a customer-centric culture within your organization.
Challenges of Customer Journey Mapping
Some challenges associated with customer journey maps may deter some businesses from using them. However, these challenges can be avoided with the right customer journey mapping platform and a team invested in customer experience success. Regardless, here are some challenges of customer journey mapping to be aware of:
Delayed ROI
Although the use of customer journey mapping is growing, few organizations have had them in use for extended periods. Only 34% of organizations have three or more years of experience developing customer experience journey maps, and 83% struggle to identify and prioritize customer experience efforts.
Effort of Integration
In a recent study, organizations that use customer journey mapping solutions said that the number one thing their provider needs to improve is the ease with which data sources are integrated. This means that these organizations may be spending too much time setting up their customer journey mapping platform or not setting it up completely and are missing out on important data that could be used to provide business insights.
Quality of Integration
Similarly, the organizations referenced above said the second most important thing for providers to fix is the quality of integrations with voice of the customer platforms, content management repositories, or other existing systems.
Journey Measurement
Another common challenge among organizations that utilize customer journey maps is the ability to measure the different phases of the customer journey and analyze their impact on business performance.
Journey Validation and Testing
When organizations create and use customer journey maps, they want to be able to validate and test them. Customer journey map testing and validation refers to the process of evaluating and verifying the accuracy and effectiveness of a customer journey map by actively testing real-world scenarios and gathering feedback.
The goal is to ensure that the journey map reflects actual customer behaviors, experiences, and pain points and that the proposed changes or optimizations will deliver the intended improvements. However, this was ranked in the top five biggest areas of improvement for customer journey mapping solutions.
Customer Journey Map Best Practices
As you go through the process of creating a customer experience journey map, you want to focus on how you are doing it as much as why you are doing it. When you build a journey map correctly, it can immediately be useful to you and your organization. If not, it will take time to fix, which will delay the benefits you will realize from using it. Here are some best practices to keep in mind when creating a customer journey map:
1. Use Quantitative and Qualitative Data
It can be easy to build a customer journey map based on the trackable actions a customer takes throughout their customer journey. However, this does not show what they felt at each stage or how they felt about certain touch points. You must combine insights from qualitative systems such as CRM systems, web analytics, and customer feedback tools and quantitative data such as surveys, interviews, and focus groups to correctly map the customer journey.
InMoment helps you combine structured and unstructured data for the most accurate customer understanding by building an omnichannel customer experience that combines data from multiple sources and can help you build the most accurate journey map available.
2. Align with Business Goals
In order to get executive support, you will need to connect your customer journey map to business goals. For example, it might be a marketing goal to increase conversion rates, but if you can say something like “increasing conversion rates by half of a percent will result in a 20% increase in revenue,” you will be more likely to secure executive support.
3. Involve Frontline Employees
When creating customer journey maps, they are usually a cross-departmental effort across marketing, sales, customer support, etc. However, the frontline employees are often left out of it even though they deal with the customer more frequently than any other department. Consider sending out an employee survey or meeting with employees to understand their view of the customer journey and the customer experience.
4. Leverage AI Customer Journey Insights
AI customer journey insights can be used to reveal hidden pain points, optimize touchpoints, and improve the customer journey flow. These insights allow your business to proactively respond to customer needs and streamline processes.
InMoment’s Strategic Insights team will use AI Journey Insights to identify the significant touchpoints in your customer feedback data. Our team helps you contextualize these findings by categorizing insights based on where they fit in the customer journey, understanding the underlying sentiment, and how insights can be implemented.
Customer Journey Map Examples
When creating a customer journey map, it may benefit your team to look at customer journey mapping examples. These examples can provide valuable insights into how different organizations across different industries have mapped their unique customer journeys.
Visualizing these examples can help your team understand how to structure the journey map, integrate data, and highlight customer pain points. Furthermore, studying a range of examples allows you to adapt best practices and innovative techniques to fit your specific customer base, whether focusing on B2B or B2C journeys. This exploration not only aids in the visual aspect but also helps pinpoint gaps in your current mapping approach that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Customer Journey Map Template
Get a free customer journey map template and begin outlining experiences and important touchpoints.
Customer Experience Journey Mapping with InMoment
InMoment’s customer experience platform gives you all the tools you need to create and use an effective customer journey map to improve your organization’s CX and financial performance. Check out InMoment’s XI Platform to see how you can uncover customer insights in every form of customer feedback to create a more efficient customer journey!
References
Khoros. Must-know customer service statistics of 2024. (https://khoros.com/blog/must-know-customer-service-statistics). Accessed 10/8/2024.
Nielsen Norman Group. Journey-Mapping Impact: Research Findings. (https://www.nngroup.com/articles/journey-mapping-impact/). Accessed 10/8/2024.
Hanover Research. How To Use Customer Journey Mapping and Improve Customer Experience. (https://www.hanoverresearch.com/insights-blog/corporate/customer-journey-mapping/). Accessed 10/8/2024.
Gartner. Gartner Says Most Customer Experience Programs are not Delivering on the Promise of Improving Differentiation and Helping Brands Better Compete. (https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/gartner-says-most-customer-experience-programs-are-not-deliverin). Accessed 10/23/2024.
Forrester. Key Trends In Customer Journey Mapping Platforms. (https://www.forrester.com/report/key-trends-in-customer-journey-mapping-platforms/RES179422). Accessed 10/10/2024.