The Impact of Prescriptive Analytics in Business Decisions

In an increasingly data-driven world, it is no longer enough to understand the past. Successful businesses utilize prescriptive analytics to aid in data-driven decisions that will improve their bottom line. Whether it’s reducing your cost to acquire a customer, decreasing your churn rate, or anything in between. Your business can use analytics to drive success and improve customer experiences.
What is Prescriptive Analytics?
Prescriptive analytics is a type of advanced analytics that focuses on providing recommendations and insights to optimize decision-making. Prescriptive analytics uses a combination of mathematical models, algorithms, and business rules to analyze data and generate recommendations. It takes into account various factors, constraints, and objectives to suggest the best course of action in a given situation. This type of analytics is particularly valuable in complex and dynamic environments where decision-makers need guidance on how to respond to different scenarios.
What is the Primary Goal of Prescriptive Analytics?
The primary goal of prescriptive analytics is to provide actionable recommendations that help organizations or individuals make informed decisions to achieve desired outcomes. Unlike descriptive analytics, which focuses on summarizing historical data, and predictive analytics, which forecasts future events, prescriptive analytics takes it a step further by suggesting the best course of action.
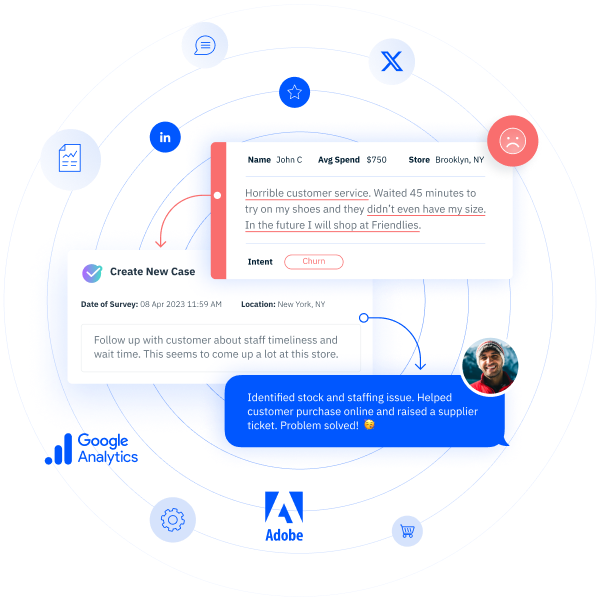
With InMoment’s award-winning XI Platform, businesses have access to comprehensive analytics and prescriptive actions represented in customizable dashboards. These tools allow your business to digest analytical insights in the way that makes the most sense for your company.
How Does Prescriptive Analytics Work?
Prescriptive analytics works by using advanced analytical techniques to recommend actions that optimize decision-making. It involves analyzing data, creating mathematical models, and considering various constraints and objectives to suggest the best course of action.
Consider a retail company using prescriptive analytics to optimize its pricing strategy. The process would involve analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and external factors. Predictive analytics forecasts the demand for products under different price points. The optimization models factor in costs, competitor prices, and revenue objectives.
The prescriptive analytics system then recommends specific pricing adjustments for each product to maximize overall revenue while considering factors like customer demand elasticity and market conditions. The recommendations are not only based on historical data and predictions but also on the optimization of pricing strategies to achieve the desired financial outcomes for the company. Decision-makers can follow these recommendations to adjust prices and potentially improve the company’s profitability.
How Does Prescriptive Analytics Differ From Other Types of Analytics?
When it comes to data analytics, organizations leverage various approaches to extract meaningful insights and guide decision-making. Each type of analytics serves a distinct purpose, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of data. There are four key types of analytics: prescriptive, predictive, diagnostic, and descriptive.
Predictive vs Prescriptive Analytics
While predictive analytics is instrumental in understanding likely future scenarios, prescriptive analytics takes it a step further by providing actionable insights that empower organizations to make optimal decisions and drive positive outcomes. Both methodologies, when used in tandem, contribute to a comprehensive and strategic approach to data-driven decision-making. Here are some key differences between the two types of analytics:
- Predictive analytics focuses on forecasting future events, while prescriptive analytics recommends actions to influence or achieve desired outcomes.
- Predictive analytics is more concerned with “what will happen,” while prescriptive analytics is concerned with “what to do about it.”
- Predictive analytics helps organizations prepare for the future, while prescriptive analytics guides decision-makers in shaping the future.
Diagnostic Analytics vs Prescriptive Analytics
Diagnostic analytics and prescriptive analytics are two distinct approaches within the realm of data analytics, each serving different purposes in the decision-making process. Diagnostic analytics is focused on understanding the reasons behind past events or performance. Diagnostic analytics helps organizations understand the factors contributing to past outcomes, prescriptive analytics empowers decision-makers with actionable recommendations to shape future events. Here is a breakdown of some differences between these two types of analytics:
- Diagnostic analytics looks backward to understand past events, while prescriptive analytics looks forward to recommending actions for future outcomes.
- Diagnostic analytics is retrospective and focused on root cause analysis, while prescriptive analytics is proactive and provides actionable insights for decision-making.
- Diagnostic analytics helps uncover the “why” behind events, while prescriptive analytics guides decision-makers on “what to do” to achieve desired results.
As an example, consider an e-commerce platform employing diagnostic analytics to investigate a sudden drop in website traffic, examining factors such as marketing campaigns, website usability, and external events.
Descriptive and Prescriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics is centered around summarizing historical data to provide a comprehensive understanding of past events and trends. It seeks to answer the question, “What has happened?” by using data aggregation, visualization, and statistical analysis to present a clear and concise overview of historical performance. Prescriptive analytics takes a more proactive stance by answering the question, “What should be done?” Integrating both approaches offers a comprehensive strategy for effective decision-making.
Consider a retail company that uses descriptive analytics to review sales reports from the previous quarter, visualizing key metrics such as total sales, product categories, and customer demographics. By integrating prescriptive analytics into the decision-making process, the retail company can move beyond analyzing past performance to actively shaping and optimizing its strategies for the future.
Advantages of Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive analytics offers several compelling advantages that make it a valuable tool for organizations seeking to optimize decision-making. One key benefit is its ability to provide actionable insights. By leveraging optimization models and algorithms, prescriptive analytics goes beyond predicting outcomes and offers specific recommendations on the best course of action. This empowers decision-makers with a clear and informed path forward, leading to more effective and strategic choices.
Another advantage is adaptability. Prescriptive analytics systems often incorporate feedback loops, allowing them to continuously learn and refine their recommendations based on new data and changing conditions. This adaptability enhances the relevance and accuracy of the insights provided, particularly in dynamic and evolving environments.
Additionally, prescriptive analytics enables organizations to consider various factors and constraints simultaneously. This holistic approach ensures that decisions align with multiple objectives, leading to outcomes that are not only optimized for a specific goal but also take into account broader organizational priorities.
Disadvantages of Prescriptive Analytics
Despite its benefits, prescriptive analytics comes with certain challenges and disadvantages. One notable concern is the complexity of implementation. Building and maintaining prescriptive analytics models requires expertise in advanced analytics, mathematics, and algorithmic development. Organizations may face obstacles in terms of the technical skills needed, as well as the resources required for ongoing maintenance.
Another challenge is the reliance on data quality. Prescriptive analytics heavily depends on accurate and relevant data. If the input data is incomplete, inaccurate, or biased, it can compromise the reliability of the recommendations. Ensuring data quality becomes a critical aspect of successful prescriptive analytics implementation.
Privacy and ethical considerations also come into play. Prescriptive analytics often involves processing sensitive information, raising concerns about data privacy and the ethical implications of decision-making based on algorithmic recommendations. Striking the right balance between data-driven insights and ethical considerations becomes essential in the deployment of prescriptive analytics.
While prescriptive analytics offers powerful advantages in guiding optimal decision-making, organizations must navigate the complexities of implementation, address data quality concerns, and carefully consider ethical implications to fully realize its potential benefits.
How Does Prescriptive Analytics Help in Business Decision-Making?
Prescriptive analytics plays a pivotal role in enhancing business decision-making by providing valuable insights and actionable recommendations. One key contribution lies in its ability to optimize choices. By leveraging sophisticated mathematical models and algorithms, prescriptive analytics evaluates multiple decision scenarios, considering various factors, constraints, and objectives. This process goes beyond predicting outcomes; it guides decision-makers on the most effective actions to take, ultimately leading to decisions that align with organizational goals.
Moreover, prescriptive analytics contributes to strategic planning and resource allocation. Organizations face numerous challenges in allocating resources efficiently, whether it’s managing production schedules, optimizing supply chain logistics, or determining marketing budgets. Prescriptive analytics analyzes complex datasets to offer recommendations that maximize efficiency, minimize costs, and improve overall resource utilization. This, in turn, enables businesses to allocate resources in a manner that yields the greatest return on investment.
Prescriptive analytics also facilitates risk management. By considering potential scenarios and their associated risks, decision-makers can make informed choices that mitigate uncertainties. Whether it’s in financial investments, supply chain disruptions, or market fluctuations, prescriptive analytics aids in identifying and addressing risks preemptively. This proactive approach empowers businesses to navigate volatile environments more effectively.
How to Get Started with Prescriptive Analytics
Implementing prescriptive analytics involves a strategic approach to harness its benefits effectively. The first step is to establish a clear understanding of organizational goals and challenges. Identify specific decision areas where prescriptive analytics can make a significant impact, such as resource allocation, supply chain optimization, or pricing strategies.
Once the focus areas are defined, the next step is to gather and prepare the necessary data. Data quality is paramount in prescriptive analytics, so organizations should ensure that they have access to accurate, relevant, and comprehensive data. Integration of data from various sources may be necessary, requiring robust data preprocessing to create a unified dataset suitable for analysis.
Collaboration between data scientists, domain experts, and decision-makers is essential throughout the process. Domain experts provide valuable insights into the contextual nuances of decision-making, while data scientists leverage their analytical expertise to build and refine prescriptive analytics models. A collaborative approach ensures that the models align with organizational objectives and are practical in real-world scenarios.
Pilot projects can be instrumental in validating the effectiveness of prescriptive analytics in a controlled environment. Start with a specific use case, implement the prescriptive analytics model, and assess the outcomes. The insights gained from the pilot project can inform adjustments and improvements before scaling up to broader applications.
Continuous monitoring and optimization are critical components of a successful prescriptive analytics initiative. Regularly review the performance of models, update them with new data, and refine algorithms based on feedback. This iterative approach ensures that the prescriptive analytics system remains adaptive and aligned with evolving business needs.
Utilize Prescriptive Analytics with InMoment
InMoment’s prescriptive analytics capabilities give your business the ability to transform raw data into strategic insights. These insights provide actionable recommendations that empower decision-makers to make informed choices and drive optimal outcomes. With the power of prescriptive analytics at your fingertips, you can not only understand historical performance but also proactively shape future strategies, enhance operational efficiency, and stay ahead of the competition in today’s dynamic business landscape. Schedule a demo to learn more today!