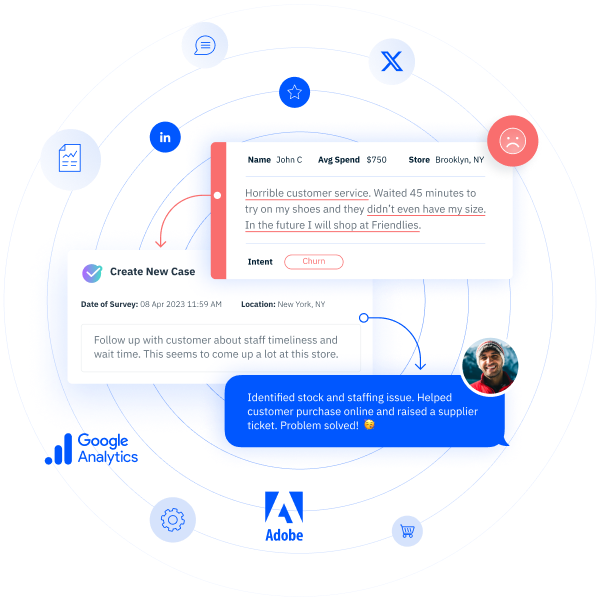
If you’ve ever heard the terms “CX” or “customer experience” before, you probably know that they and similar phrases refer to organizations’ attempts to scour every interaction for feedback and insights. You might also know that customer experience is generally considered to be a more specific subset of user experience (UX). But how do those organizations design CX programs? What goes into deciding which interactions to scrutinize, the goals formed around that work, and so much more? If you’re curious about CX design and how organizations wield it, you’ve come to the right place!
Today’s discussion breaks down the wider universe of CX design, but we’re also going to talk about the best ways for organizations to leverage this discipline. Many brands consider merely “managing” experiences to be the finish line of CX design, but there’s a lot more that organizations can accomplish, including genuine Experience Improvement (XI). Let’s get into it!
What Is CX Design?
The idea of CX design was relatively simple for many years. Basically, when an organization’s leadership decided to engage in customer experience design, they would deploy surveys (sometimes physically) for customers to fill out and hand back. We’ve all seen the little surveys that sometimes pop up after buying a sandwich, getting a car serviced, visiting a retailer, and the like. For a long time, this was considered cutting-edge CX technology and a valuable means of soliciting feedback. Other methods, like mystery shopping, were often used as well.
However, as technology has grown more sophisticated, so too has our understanding of not just how to manage customer experience, but how to improve it. Our understanding of what customers truly seek in experiences has broadened as well, and so the job of a CX designer (and the role of CX strategy in general) became more about understanding customers’ minds, not just getting their feedback. It became about optimizing journey touchpoints to delight customers and nurture relationships!
Unfortunately, even though technology and new learnings have made CX design so much more powerful than in years past, many organizations seem content to use it to gather numbers and react to problems only as they arise. This principle is reflected in how these companies’ programs are designed; CX teams don’t deploy to fix a problem until it’s been submitted by a customer, and discussions on program progress are centered around how today’s metrics compare to yesterday’s.
The issue with this sort of CX design is that while it can give you a superficial temperature reading of how customers like your brand… that’s about all you’re getting from it. Organizations that take this tack with their CX design miss opportunities to, yes, fix glaring flaws, but also meaningfully improve experiences and get to know their customers on a more human level. That is where the true power of CX design comes into play, and the brands that wield it are, more often than not, at the top of their vertical because of it.
What Does the CX Design Process Look Like?
If CX design can really help organizations achieve such dramatic transformations and high goals, what’s the first step toward actually doing that?
As we mentioned earlier, many brands start their CX design process by looking at a handful of channels their customers might use to communicate (contact centers, social media, etc.) and deciding to pay more attention to those channels. However, while going about CX design this way might net you a few insights here and there, it’s actually much more effective to design with the end in mind.
In other words, before you even turn any of your listening posts on, take some time to consider which goals you actually want to achieve with your CX program. The sky’s the limit, too! Don’t be afraid to stake out some truly ambitious goals in your design. Experience programs can be used to achieve some pretty amazing things.
What those things are depends on what your business needs. For example, if your customers are churning a lot more than you’d like, you can build your CX design around better customer retention. Or, perhaps you’d like to use your experience program to improve workplace culture or get a better sense of what’s going on in the marketplace around your organization.
Whatever your Experience Improvement goal is, just having that as a guiding ethos will make a world of difference for your CX design. However, while your goal should be aspirational, it also needs to be quantifiable—to revisit the churn example, make sure that you tie a specific percentage or number to your goal. That will further define the finish line you want your CX program to help you cross, and it will also make your initiative’s value more tangible and therefore more visible!
Why Is CX Design Important?
Once organizations establish the goal(s) they want to achieve with their CX design and attach some sort of target number to it, it’s time to take the next step and consider which CX tools to use. This is another reason why setting a goal before doing anything else is so helpful, because it helps you determine not just which tools and channels to focus on, but also which groups of customers.
For example, if you see a chance to improve new customer acquisition, it doesn’t make sense to deploy tools geared for that goal toward all of your customer segments. Rather, you can free yourself and your CX design to focus all your efforts towards new customers. And if you have the bandwidth for additional CX goals, you can deploy your remaining tools where they most make sense. This more deliberate and thoughtful approach to design goes a long way toward achieving those goals!
This approach will also help you find and listen to the channels most relevant to your CX goals. To revisit the customer acquisition example, a CX team that sets that goal might research the areas where new customers most talk about your brand, then set up surveys and other listening tools there to capture that customer intelligence at its most organic. The team will have honed in on the channel most relevant to its goals and successfully filtered out noise from customer segments that are less relevant to those goals.
You don’t have to be a CX expert to know that brands and organizations love data. In fact, some companies love data so much that they gather it just for the sake of having it! Having data is certainly important, of course, but much like the CX metrics we talked about earlier, just having it won’t create Experience Improvement for your customers. The only way to do that is to actually take that data and mine it for valuable insights.
Data hygiene is yet another area that conventional CX design struggles with. A lot of programs are designed to gather lots of data very efficiently, but that creates a whole new challenge for the people running that program—namely, how much time does it take to sift through a mountain of data? What insights should CX teams look for and which ones should they disregard? And how can those teams make progress finding insights when their program is gathering data from every corner at every moment?
This is yet another reason why a deliberate, more targeted approach to CX design is the way to go. If you build your CX programs around very specific goals, the data you gather will be much more specific as well. Your data mountain will be smaller and more manageable, and your CX team won’t have to go near as far to find the insights most helpful to their goals.
One final note about data is that it doesn’t have to come from the CX team alone. Pulling other employees and groups into your CX design process can help you get a complete, 360-degree picture of your customer, further cementing both your goals and your future success. Including others also lets them know that, no matter how far away their job may be from the front lines, their work still matters and is relevant to creating a great experience for customers.
Realizing Experience Improvement Through CX Design
This is the hardest part of customer experience design, but it’s also what the process that we’ve been talking about is designed to simplify for you, your CX team, and your entire brand. You’ve used this CX design process to learn what you need to change to create Experience Improvement for your customers; now it’s time to reach out to the right teams and work together to actually make those alignments.
Once you do, continue to track and quantify those changes. Quantifiable goals are like receipts for a CX program; they give you something to prove its worth when you go back to the board for additional funding (as a quick aside, if you hear any positive customer stories that come about as a result of your changes, save those too! Execs love them). Some changes take a while to blossom, but they’ll be worth the wait once they come through.
Ultimately, what is the point of great CX design? A stronger bottom line for your brand? Yes. Eliminating problems with your journey touchpoints? Absolutely! But there’s an even more ambitious goal that comes about as a result of great CX design, and that’s true Experience Improvement. In this context, Experience Improvement doesn’t just refer to individual interactions better and fixing journey touchpoints (though those are certainly important). It means aligning brand and CX design to achieve seamless experiences. It means understanding who your customers are on a deeply fundamental, human level.
Once organizations achieve that close-up understanding of their customers and thus a close bond with them, there’s almost nothing that can break that relationship. Customers who feel understood as human beings, not just clients, won’t ditch you for a competitor. They’ll evangelize your brand to anyone who will listen. And it’ll all be thanks to your stellar CX design and the Experience Improvement opportunities it created!
We hope that this conversation has given you more insights into what CX design is and how fundamentally it can transform your experiences and brand ecosystem. If you want to learn more about how Experience Improvement can help your organization, feel free to download this e-book!
We’re always up for chatting about all things experience, and our mission is to help you own the moments that matter.