The Net Promoter Score (NPS) Guide
The Net Promoter Score is a customer experience metric that measures customer satisfaction and loyalty. A Net Promoter Score can be calculated after categorizing how customers respond to the question “On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely are you to recommend our product/service to a friend or coworker?”
What is Net Promoter Score (NPS)?
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a trademarked metric between -100 and 100 that measures the likelihood of a company’s customers promoting the brand through new customer references and repeat business. The higher the score the more likely your customers will promote your brand.
NPS also stands for the Net Promoter System®, a trademarked system and framework that was built around the Net Promoter Score. It is a model that tries to tie a corporation’s bottom line with its customer’s happiness and satisfaction with its products and services. This system aims at managing corporate profits and sustainability through a customer experience lens.
Before you calculate your Net Promoter Score, you need to understand the three segments your customers will be divided into: detractors, passives, and promoters.
- Detractors: These customers respond to surveys in a way that indicates they would not recommend your product or service to others. They are usually grouped as anyone responded who responded 0-6 on the scale.
- Passives: Passive customers represent customers who responded neutral to a survey about your product or service, indicating that they would not recommend it nor would they advise against it. They are generally categorized as responding either 7 or 8 on the scale.
- Promoters: Promoters represent your most loyal customers, and answer either 9 or 10 on the scale. These customers are extremely likely to recommend your product or service to others

Transactional vs Relational Net Promoter Scores
When implementing Net Promoter Scores (NPS), businesses can choose between two primary approaches: Transactional NPS and Relational NPS. Understanding the differences between these two types is crucial for leveraging NPS effectively to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Transactional NPS
Transactional NPS measures customer satisfaction and loyalty based on specific interactions or transactions with the company. It is typically collected shortly after a customer completes a particular transaction, such as a purchase, a customer service interaction, or a product delivery.
For example, a retail brand might send an NPS survey to customers shortly after they make a purchase online or visit a store. The feedback received helps the company understand the effectiveness of their checkout process, delivery service, or in-store experience.
Relational NPS
Relational NPS, on the other hand, measures overall customer loyalty and satisfaction with the brand or company over a longer period. It assesses the customer’s broader relationship with the business rather than focusing on individual transactions.
For example, the same retail brand might send an NPS survey to their entire customer base once a year to assess the general satisfaction and loyalty of their customers. This feedback helps the company understand their position in the market and identify areas for strategic improvement.
The choice between Transactional and Relational NPS depends on the business’s goals and the specific insights they seek to gain. Many companies find value in using both approaches in tandem, as they provide complementary insights. Transactional NPS offers immediate, actionable feedback on specific interactions, while relational NPS delivers a broader view of overall customer loyalty and brand perception.
Why NPS Score is Important
The Net Promoter Score (NPS) has become a crucial metric for businesses seeking to understand and improve customer satisfaction. This single number, derived from a simple question, holds significant value for several reasons:
1. Customer Loyalty Indicator
The primary purpose of NPS is to gauge customer loyalty. By asking customers how likely they are to recommend a product or service to others, businesses can identify their most loyal advocates. A high NPS indicates satisfied customers who are not only likely to make repeat purchases but also to actively promote the brand.
2. Word-of-Mouth Marketing
Customers who give high NPS ratings are more likely to engage in positive word-of-mouth marketing. The increased importance of social media marketing has made it more crucial than ever for loyal customers to be brand ambassadors. A high NPS score is reflective of your customers’ willingness to use those channels to promote your brand and bring in new customers.
3. Identifying Areas for Improvement
While a high NPS is desirable, a low score can be equally valuable. It serves as an alert that something may be amiss in the customer experience. Businesses can use this feedback to identify specific pain points and address issues that might be hindering customer satisfaction and loyalty.
4. Benchmarking Against Competitors
NPS allows businesses to benchmark themselves against industry competitors. Understanding where your NPS stands in comparison to others in the market provides valuable context. It can inspire a drive for continuous improvement and innovation to stay ahead in the competitive landscape.
5. Predictive Business Growth
Research has shown a strong correlation between high NPS and business growth. A recent study showed that a company with the highest Net Promoter Score in its industry outgrew its competitors by more than two times.
Satisfied customers not only tend to make more purchases themselves but also contribute to the growth of the customer base through referrals. NPS, therefore, becomes a leading indicator of future business success.
What Are the Benefits of Net Promoter Score?
The Net Promoter Score is one of the most popular customer experience metrics for a reason. The benefits of regularly utilizing it can improve your customer experience and business performance. Here are some of the most common benefits of the Net Promoter Score:
1. Simplicity
The Net Promoter Score is a simple and direct question. Because of its simplicity, it is easy to implement and analyze. Perhaps most importantly, your customers will have no problem understanding it. Regardless of industry or demographic, every customer will be able to answer the Net Promoter Score question.
2. Cost-Effective
NPS surveys are relatively low-cost to administer compared to more comprehensive market research methods. They can be easily integrated into regular customer touchpoints like post-purchase emails or service follow-ups.
3. Increased Employee Engagement
In the workplace, the importance of employee loyalty and engagement cannot be understated. When your business uses the Net Promoter Score as a measure of customer experience, it is easy to get employees on board. Regardless of their position within the company, employees will have an easier time focusing on the performance of one number as opposed to multiple metrics.
Sharing NPS results with employees can foster a culture of continuous improvement and customer focus. It can also help in aligning the organization towards common goals of enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
How to Calculate Net Promoter Score
In order to calculate your Net Promoter Score, you first need results from a Net Promoter Score Survey. Once you have the results from that survey or series of surveys, you will be able to categorize your respondents into promoters, passives, and detractors.
Once those two steps are completed, the actual calculation is very simple: subtract the percentage of detractors from the percentage of promoters. To visualize it, it should look like:

For example, consider a retail brand that was interested in finding out their Net Promoter Score.
They conducted a survey of 1,000 of their recent customers. The responses were categorized into promoters (those who rated 9-10), passives (those who rated 7-8), and detractors (those who rated 0-6).
The survey results showed that 200 customers were promoters, 300 were passives, and 500 were Detractors. To calculate the NPS, this brand determined the percentages of Promoters and Detractors, which were 20% and 50%, respectively. The NPS was then calculated by subtracting the percentage of Detractors from the rate of Promoters, resulting in an NPS of -30. This negative score indicated that a significant number of customers were dissatisfied and unlikely to recommend the brand.
What is a Good Net Promoter Score?
Understanding what constitutes a “good” Net Promoter Score can be crucial for businesses aiming to gauge customer loyalty and satisfaction effectively. However, interpreting NPS results isn’t always straightforward, as a “good” score can vary widely across industries and contexts. Here are key considerations to help determine what a good NPS might look like for your business:
Net Promoter Score Benchmarks by Industries
A good NPS often depends on the industry in which a business operates. Different sectors have varying average scores due to the nature of their products, services, and customer expectations. For example:
- Auto dealers have an average NPS score of 39
- Hotels have an average NPS score of 33
- Banks have an average NPS score of 21
- Department and specialty stores have an average NPS score of 62
Pharmacies and Drug Stores
Walmart pharmacies have an NPS score of +32. Given that the highest possible score is +100, this score may seem just average. However, the customer experience team at Walmart is likely thrilled, as this is one of the highest NPS scores in the drug store and pharmacy industry.
Technology and Software
Comparing the software industry, where the average NPS is +34. Leading companies in this sector, like Salesforce (+66) and Adobe (+62), have NPS scores in the +60 range.
For the laptop computer industry, where the average NPS is +43. Considering Apple’s strong brand reputation and customer loyalty, can you guess their NPS for their popular MacBook?
Apple’s MacBook has been reported to have an NPS of +62. You likely guessed close to this figure, knowing the industry average. This illustrates why comparing scores within industries is more insightful than using an absolute scale.
Competitor Analysis
A good NPS should also be assessed relative to competitors. Knowing where your business stands in comparison to industry peers can provide a more accurate picture of performance. If your NPS is above the industry average, it typically indicates strong customer loyalty and satisfaction. For instance, if the industry average is 25 and your score is 35, you’re likely outperforming competitors in customer satisfaction.
Company Goals
A good NPS should align with your company’s specific goals and customer expectations. Businesses with high customer service standards might aim for scores above 50, while others might set more modest goals based on realistic assessments of their current situation. For instance, a company known for exceptional service might consider an NPS below 50 as a sign of needing improvement, whereas a business in a challenging market might be satisfied with a score around 20.
Ultimately, setting realistic NPS targets based on historical data, industry standards, and business goals is essential. Companies should aim for steady improvement rather than focusing solely on achieving a specific score. For example, if your current NPS is 10, setting a goal to reach 20 in the next year can be both challenging and achievable, motivating your team to implement effective customer experience enhancements.
How to Improve Your Net Promoter Score
There is no shortcut to improving your Net Promoter Score. To improve your net promoter score, you need an effective customer experience strategy, proactive measures, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Here are five things you can start doing to improve your NPS:
1. Understand Customer Feedback
Start by thoroughly analyzing customer feedback. Whether positive or negative, every comment holds valuable insights into what customers appreciate and where improvements can be made. Use this understanding as the foundation for your improvement initiatives.
2. Address Detractor Feedback Promptly
Detractors, customers who give low scores, are an immediate priority. Identify common issues raised by Detractors and develop strategies to address them promptly. Demonstrating a commitment to resolving customer concerns can turn Detractors into satisfied customers.
3. Celebrate and Amplify Promoters
Promoters are your brand advocates, and their positive feedback is invaluable. Acknowledge and appreciate Promoters by amplifying their testimonials, featuring them in marketing materials, and expressing gratitude. This not only strengthens customer relationships but also attracts new customers through positive word-of-mouth.
4. Implement Customer Suggestions
Act on actionable suggestions provided by customers. If multiple customers highlight a specific area for improvement, consider it a strategic opportunity to enhance your offerings. Implementing customer-driven changes demonstrates responsiveness and a commitment to delivering what your audience truly values.
5. Personalize Customer Experiences
Tailor your interactions to individual customer preferences and needs. Leverage data and analytics to understand customer behavior, history, and preferences. Personalized experiences contribute to a positive perception of your brand, fostering loyalty and increasing the likelihood of receiving higher NPS scores.
How to Create a Net Promoter Score Survey
There are multiple ways to craft a Net Promoter Score survey. The survey itself is simple, but in order to get effective feedback from your customers you will need to make sure that your survey design is executed in a way that sets your business up for success.
1. Define the Purpose
Before designing your survey, clearly define its purpose. Determine what you aim to learn from your customers and how the feedback will be used to improve your business. For example, are you building a transactional NPS survey? Or a relational one? This helps in crafting relevant questions and analyzing results effectively.
2. Craft the Core NPS Question
The core of any NPS survey is the primary question: “On a scale of 0-10, how likely are you to recommend our product/service to a friend or colleague?”
This question should be simple, direct, and focused on gauging customer loyalty and the likelihood of recommending your brand.

3. Add a Follow-Up Question
To gain deeper insights, include an open-ended follow-up question such as: “What is the primary reason for your score?”
This question allows customers to provide specific, qualitative feedback and elaborate on their rating. This offers valuable context that can highlight strengths and areas for improvement.
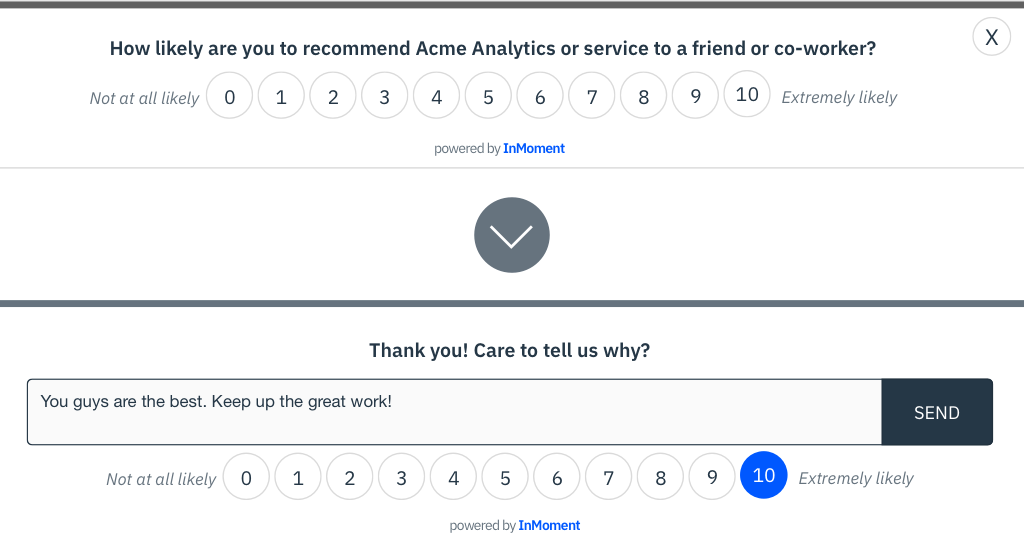
4. Choose the Right Timing
Timing is crucial for obtaining accurate feedback. For transactional NPS surveys, send the survey shortly after a customer interaction, such as a purchase or service call. For relational NPS surveys, conduct the survey at regular intervals, such as quarterly or annually, to gauge overall satisfaction and loyalty over time.
5. Deploy the Survey
Send the survey across the appropriate channels, and then monitor feedback and response rates. Based on the answers to the survey, you may realize there are cases that require immediate attention. For example, a customer may rate you as a 0 and then in the follow-up question explain how they were overcharged for an item. Below is an example of what an NPS survey may look like when sent via email:

How Often Should I Send Net Promoter Score Surveys?
Determining the frequency of NPS surveys is a crucial aspect of maximizing the utility of this valuable metric while respecting your customers’ time and attention. Striking the right balance ensures that you receive timely feedback without causing survey fatigue. Consider the following factors when deciding how often to send NPS surveys:
1. Transaction Frequency
Align the frequency of NPS surveys with the frequency of customer transactions. For businesses with frequent customer interactions, such as e-commerce platforms or subscription services, more regular surveys may be appropriate. Conversely, for businesses with less frequent transactions, a less frequent survey schedule may be sufficient.
2. Customer Lifecycle Events
Tie NPS surveys to key events in the customer lifecycle. Sending surveys after significant touchpoints, such as a purchase, customer support interaction, or product usage milestone, provides contextual feedback. This targeted approach allows you to capture insights when the customer’s experience is most relevant.
3. Product or Service Changes
Introduce NPS surveys when there are substantial changes to your product or service. This could include the launch of new features, updates, or modifications to existing offerings. Monitoring NPS during these periods can help gauge customer reactions and identify areas that may require further attention.
4. Seasonal Considerations
Take into account seasonal variations in your business. Some industries experience peak seasons or specific periods of increased customer activity. Adjust your survey frequency to align with these patterns, ensuring that you capture feedback when it is most representative of customer experiences.
5. Strategic Planning Cycles
Incorporate NPS surveys into your strategic planning cycles. Conduct surveys at intervals that align with your business planning and decision-making processes. This allows you to use NPS data to inform strategic decisions and track the impact of initiatives over time.
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to how often you should send NPS surveys. It depends on your specific business context, customer interactions, and strategic objectives. By thoughtfully considering these factors, you can establish a survey cadence that maximizes the benefits of NPS while respecting your customers’ experience.
What are the Disadvantages of Net Promoter Score?
While the Net Promoter Score can have many benefits for companies, it is not without potential drawbacks. These drawbacks can be alleviated by implementing an integrated customer experience and going beyond the survey feedback received from your customers. Regardless, these are the disadvantages of the Net Promoter Score that you need to be aware of:
1. Oversimplification & Lack of Context
The Net Promoter Score reduces customer sentiment to a single number, which can oversimplify complex customer experiences and motivations. It may not capture the full breadth of customer opinions and feelings.
The NPS score alone doesn’t provide detailed reasons behind customer ratings. Without follow-up questions or additional qualitative feedback, it can be challenging to understand the specific factors influencing customer satisfaction or dissatisfaction.
2. Response Bias
Net Promoter Score surveys have the potential to suffer from response bias. This may happen because only extremely happy or unhappy customers are most likely to respond, which can lead to a skewed representation of your customer base. Because of this, your passive customers are likely to be underrepresented.
3. Survey Fatigue
Frequently administered NPS surveys can result in survey fatigue. If your customers suffer from survey fatigue, this will diminish your response rates and the quality of your customer feedback. Over-surveying can also negatively impact the customer experience.
How to Analyze NPS Scores
Analyzing Net Promoter Scores (NPS) goes beyond simply calculating the number; it involves a thoughtful examination of customer sentiments and the factors influencing their experiences. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to effectively analyze NPS scores:
1. Segment for Deeper Insights
Using NPS software, you can segment your NPS data by customer demographics, product or service usage, or even the customer sentiment associated with the score itself. This segmentation allows you to identify specific areas for improvement and tailor strategies to different customer groups.

2. Understand the Distribution
Analyze the distribution of promoters, passives, and detractors within your customer base. A skewed distribution towards promoters is positive, while an overrepresentation of detractors signals potential issues. Understanding the balance provides context for interpreting the overall score.
3. Focus on Detractors
Prioritize the analysis of detractors as their feedback indicates areas that need urgent attention. Identify recurring issues, address them systematically, and use the feedback as a roadmap for improvement. Turning Detractors into satisfied customers can have a significant positive impact on your NPS.
4. Analyze Verbatim Feedback
Dive into the qualitative feedback provided by customers alongside their NPS scores. Pay attention to common themes and specific comments. This qualitative data provides context for the numerical scores and helps identify specific pain points or areas of excellence.
5. Link NPS to Operational Metrics
Connect NPS data with operational metrics such as customer retention, conversion rates, and revenue. Analyzing these correlations helps establish a direct link between customer satisfaction and key business outcomes, reinforcing the importance of customer-centric strategies.
The more data that can be developed along with the NPS score, the more you’ll be able to understand your customer and what influences their opinions and feelings.
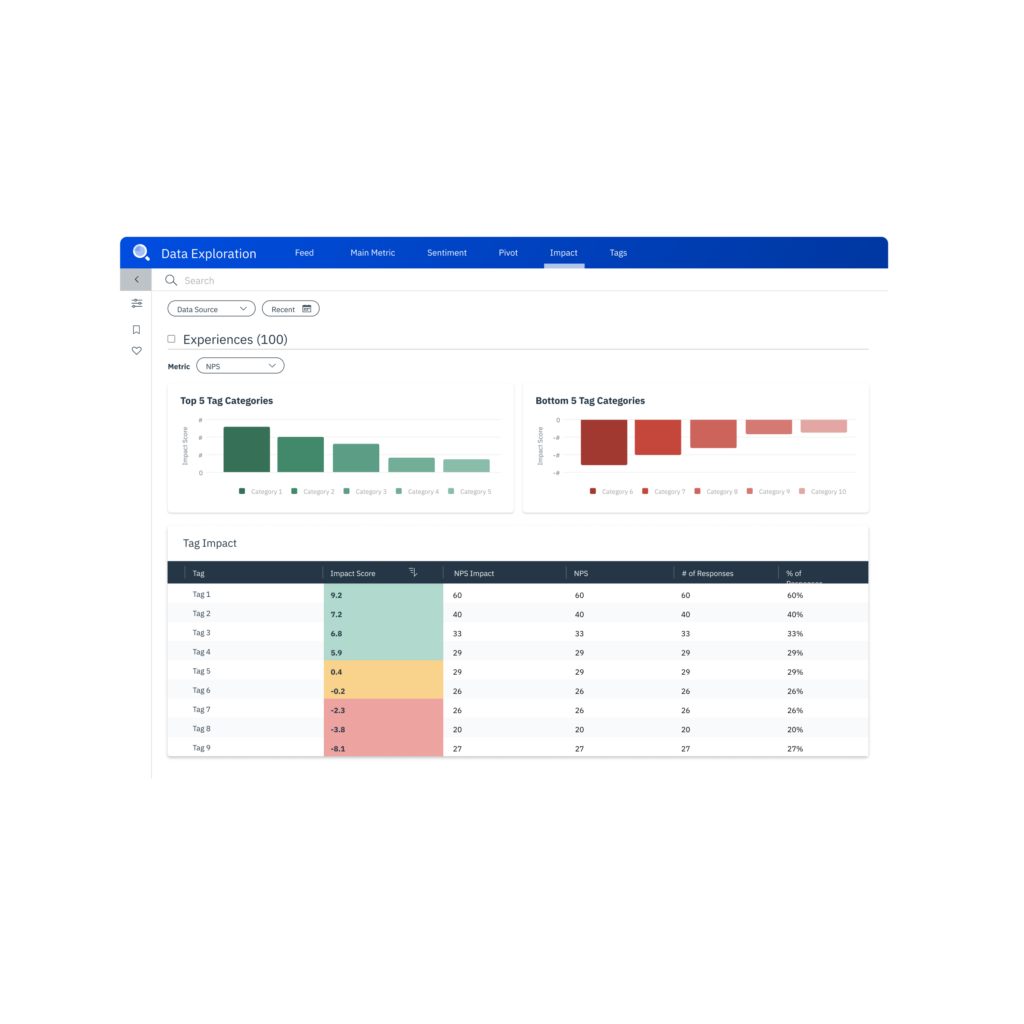
When reading NPS graph results, you’ll typically break each variable into promoters, detractors, and neutral units, then monitor how they change over time.
How to Report and Share Net Promoter Score
After analyzing, you’ll want to regularly report numbers to the rest of your CX team. Share NPS alongside other monthly or quarterly metrics such as revenue, new customers, and customer churn. To make the most out of your analysis and be able to share the store with your team and executives, here are some best practices to report your net promoter score:
Focus on Improving Your NPS Score Over Time
Rather than fixating on your score in the absolute sense, view NPS as a trend over several periods as if you were looking at stock prices. NPS scores cannot be fixed overnight, it takes time to improve.
Identify Business Goals of your NPS Program
To properly measure and align your NPS program, you’ll want to determine the business goals you want to achieve with your NPS strategy and report your net promoter score in relation to those goals. A good example is if your business is trying to improve retention, then you’ll want to report NPS alongside with churn data.

Focus on Trending Topics in Verbatim Responses
Discussing these topics will provide valuable insights into what matters most to your customers and the challenges they face. Share both the positive and negative feedback from customers with your internal stakeholders. This will enable you to address these issues and improve the overall customer experience. For startups, it’s recommended to read and respond to every single comment.
Segment Your Net Promoter Score by Relevant Customer Groups
Segmenting your customers will help you pay close attention to groups that are critical to your business success. You can segment groups by geography, size or frequency of purchase or any other attributes that drives your business. For example, a SaaS company may segment their customers by user roles and dive deeper into their experience by each group.
Use Industry Leader NPS as Benchmark for Comparison
Aiming for a perfect 100 Net Promoter Score is an admirable goal, but it can be extremely challenging to achieve. Even well-known companies with highly loyal customers rarely reach this level, and good NPS scores can vary by industry. Therefore, when setting an NPS goal for your business, choose a company within your industry that you admire and use their score as an aspirational benchmark. This will make your goals realistic and attainable within your own industry. Many companies share their NPS scores in research and reports, such as those from the Fortune 500, providing a useful resource for setting your benchmark.
Improve Your NPS with InMoment
InMoment’s XI platform gives you the ability to measure and analyze your Net Promoter Score, as well as any other metric you might use. This approach gives you the ability to create dashboards so what you see is most important to you, design and send surveys, and close the loop with customers. Schedule a demo to see what InMoment can do for you!
References
Bain & Company. How the Net Promoter Score℠ Relates to Growth. (https://www.netpromotersystem.com/about/how-net-promoter-score-relates-to-growth/). Accessed 7/9/2024.
LinkedIn. Temkin Group’s Annual Net Promoter Score Benchmark Study. (https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/temkin-groups-annual-net-promoter-score-benchmark-bruce-temkin-ccxp/) Accessed 7/11/2024.
NICE. Net Promoter Benchmarcks. (https://info.nice.com/rs/338-EJP-431/images/NICE-Satmetrix-infographic-2018-b2c-nps-benchmarks-050418.pdf) Accessed 7/30/24.
Quora. What are the best NPS (Net Promoter Score®) results for B2B SaaS companies? (https://www.quora.com/What-are-the-best-NPS-Net-Promoter-Score%C2%AE-results-for-B2B-SaaS-companies) Accessed 7/30/24.
Experience Benchmarks. 7 Apple NPS Benchmarks in 2023. (https://customergauge.com/benchmarks/blog/4-key-ingredients-fuelling-apples-high-net-promoter-score) Accessed 7/30/24.


