Of all the inevitable frustrations that come with doing business, perhaps none are so consistent as customer churn. Though countless organizations have made churn reduction a continuous goal, seeing customers leave in spite of your best efforts can be quite a headache in multiple arenas—building loyalty, evaluating effectiveness, and of course, creating a stronger bottom line.
Today’s conversation will be a quick rundown of some of the biggest reasons customers leave and what your organization can do about it. We’ll cover the churn you can control, the churn you cannot, and how to boost your own churn reduction efforts.
The Churn You Can’t Control
Let’s get this out of the way first thing—some churn is beyond any organization’s control. No matter how proactive your customer experience (CX) team is, some amount of churn is inevitable and to be expected. It’s unfortunate, but it’s also a fact of doing business.
Why might some customers invariably leave your brand? Sometimes, they really just don’t need whatever product or service you’re offering anymore. In other instances they might fall on hard times and no longer be able to buy what you’re selling. If your brand serves one or a few given areas, they might move beyond that radius and thus cut themselves off that way. All of these things are beyond your brand’s control.
However, none of this means that brands should throw their hands up in frustration. It certainly doesn’t mean your organization shouldn’t focus on churn reduction.. While some fraction of churn may be unavoidable, quite a bit of it can be controlled and can be managed by organizations. This brings us to our next point: the churn you can manage.
The Churn You Can Control
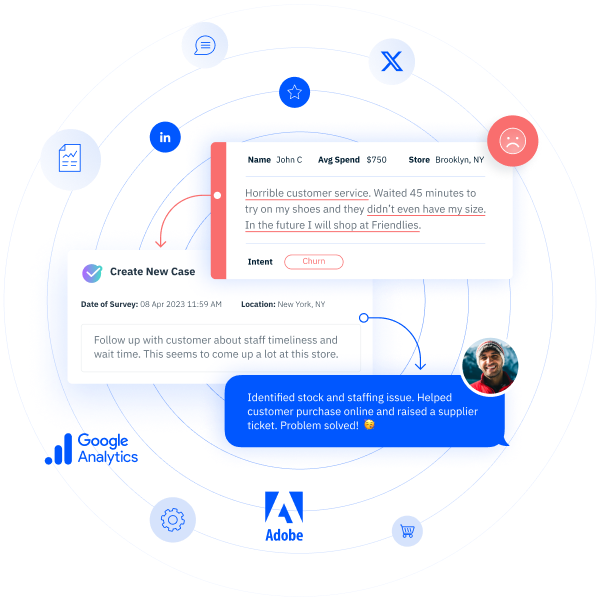
Brands can and should use customer experience programs to manage the churn they can influence, as well as evaluate what they could’ve done better. For the most part, controllable churn occurs when your product isn’t a great fit for a customer’s needs, poor communication occurs, or a myriad of other possible causes. However, your brand can respond to and control these issues.
Your customers can use feedback tools to bring problems like poor service experiences directly to brands’ attention. Organizations can then digest the feedback and formulate an action plan to combat that problem. Other churn catalysts like superior competition, product and services disconnects, or deficient employee training can be brought to light this way, as well.
Taking Action
Learning about preventable churn through a customer experience program is powerful stuff, but brands can’t stop at knowing about churn catalysts if they want to retain customers. Rather, brands need to design their programs around the audiences from whom they hope to glean intel about churn causes, listen carefully to those individuals, understand the common sentiments amid all the feedback, and then transform the business accordingly.
With this method, brands can realize a lower rate of churn for themselves and continuously apply customer feedback toward that goal. This process can help brands get churn out of the way of their goals: a better experience for all and a stronger bottom line.
Interested in learning more about reducing customer churn? Click here to read my full-length point of view on the subject and to learn additional strategies for reducing churn at your organization.