7 Steps and Tools to Avoid Brand Erosion During Organizational Transformation

Editor’s note: This is a chapter from the ebook, Unlock the Value of CX. You can download the entire book here.
Most organizations strive to ingrain in their employees a set of organizational values–behaviors and attitudes–that are the guiding principles for all employee actions. These values are often expressed as brand promises–statements about what an organization is, what it stands for, and what it will deliver to its customers.
Brand promises can be implied as well as expressed, if customers are used to a particular level of service based on their previous interactions with the company. Brand promises work best when they are realistic and actionable, targeted to the organization’s customer base and clearly linked to every customer interaction across the organization.
Meeting Brand Expectations at Every Level
The ability to meet brand promises at every customer interaction, however, eludes too many organizations. Brand promises are often set from the top of the organization and performance metrics for executives are often tied to them. However, when it comes to brand behaviors being practiced at the point of customer interaction, the results are not always consistent or satisfactory. This causes some customers to leave the interaction disappointed and frustrated.
The problem is often magnified in companies undergoing changes. As organizations grow, they often reach a state where they develop competing priorities such as, a need to cut spending to reach profitability targets or a mandate to introduce a new product or benefit.
Executives often fail to question whether changes across the organization will impact their ability to deliver on the existing brand promise. The impact is not limited to marketing or product functions. Changes to any function should be considered in terms of its downstream customer impact. Every function, from marketing, product, risk, operations and finance to human resources and compliance, has a role in fulfilling the brand promise. Each function must own its impact on the customer experience.
Take for example, a bank’s underwriting department. As a result of a recent audit, is now required to perform manager-level reviews of a greater percentage of applications prior to approval. If the leaders collectively fail to ask for more underwriting managers, the approval timeline for applications will increase, and the trickle-down impact will likely be severe. If the product and marketing teams at individual branches are not informed about this change, customer complaints will begin to build and customer satisfaction will suffer.
Seven Strategies to Prevent Brand Erosion During Organizational Transformation
The solution requires ownership by the entire organization. Below are seven strategies to avoid setting brand promises that are untenable and avoiding brand promise erosion when organizational changes happen.
1. SET THE TONE FROM THE TOP. Brand promises are often built by a chief marketing officer or branding executive in conjunction with a branding agency. However, every executive function should be involved in this effort to confirm the positioning is feasible. Once alignment exists around the brand promise, the CEO must set the tone. It is imperative for employees to be empowered to deliver on the brand promise at every customer interaction.
2. APPOINT A CHIEF CUSTOMER OFFICER. A chief customer officer is part marketer, part ombudsman, part efficiency expert and part operations expert – and fully committed to the customer journey. The best CCO is often someone experienced across various functions who can support the customer journey design from multiple perspectives. This customer champion must be willing and able to converse with peers from across the organization to ensure alignment with the brand promises, develop and lead efforts to assess impacts on the customer journey, and influence every other function to achieve the end goal of delivering the brand promises.
3. DESIGNATE A CUSTOMER COMMITTEE. It is common for organizations to have corporate committees, often aligned with executive functions, to support efforts ranging from compliance to risk to finance. A customer committee, consisting of cross-functional senior executives, will similarly support the customer experience effort and provide it with the emphasis it deserves.
4. ENGAGE IN CUSTOMER JOURNEY MAPPING. Create a cross-functional team consisting of product, marketing, risk, technology, operations, finance, human resources and other key functions to engage in exercises that map the actual customer experience. This may include what customers are trying to do, what they are feeling, what is going on behind the scenes in operations and technology, what moments of surprise, delight or unnecessary friction exist, and which interactions meet or fail to meet the brand promises. Then, develop a target customer journey that meets the brand promises with the appropriate level of friction, and chart a road map to achieve it. Think about the impacts on people (customers and employees), process, product and technology. The customer journey map should be owned by the chief customer officer and each key stakeholder in the journey. It should be updated each time a change to people, process, product or technology is considered.
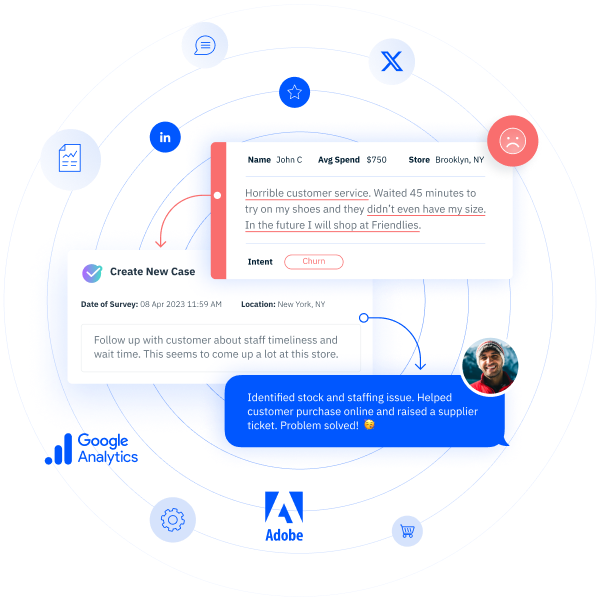
5. MEASURE CUSTOMER SATISFACTION AND CLOSE THE FEEDBACK LOOP. Many, if not most, organizations have invested in customer satisfaction monitoring of one type or another and implemented scoring methodologies with which to keep track. However, monitoring alone won’t move the needle on customer satisfaction. The keys to the success of customer satisfaction monitoring are 1) implementation of a feedback loop, and 2) understanding drivers behind changes in macro-level satisfaction scores. Qualitative information about a poor experience (a low score) from a customer is an indicator that something has gone wrong. When multiple survey responses are similar, that’s an indicator that a process is broken. It is important that organizations not only monitor feedback but also assign owners of the feedback loop for each key step in the journey. When a customer provides negative feedback, the journey owner must reach out to the customer, acknowledge the issue and commit to a response. They must then investigate, engage in internal communication, develop a plan to rectify problems (if needed) and follow up with the customer.
6. DEVELOP CUSTOMER SATISFACTION METRICS ACROSS THE ORGANIZATION. Companies should develop meaningful and consistent customer satisfaction metrics for employees that tie directly to compensation. A technology metric, such as system uptime for example, does not correlate to customer experience. Although system uptime is clearly a requirement for customer satisfaction, it is too narrow. Rather, develop organization-wide metrics that apply to all employees and allow them to relate the requirement to their own tasks.
7. LEVERAGE INDEPENDENT TESTING. Independent testing is crucial to ensure what you have prescribed is actually occurring. Independent testers should be given tasks tied to discrete journeys and asked to report back on exactly what happened and how they felt as a result of the experience. Additionally, testers should provide a fact-based method for comparing the interaction against the journey map and brand pillars, as well as qualitative feedback that uncovers gaps between the experience and the brand promises. Achieving excellence in customer experience is a result of every employee living the organization’s brand promise. Getting there requires significant enterprise-wide commitment, including the implementation of the steps listed above. In return it can reap significant rewards in the form of satisfied customers, happier employees, greater revenues and improved profitability.