Most comprehensive customer experience programs are made up of several different types of studies, the two most common of which are Transactional and Relationship studies. Here we will describe the differences between these two types of studies.
Transactional or trigger-based studies are the base of most customer experience programs. This type of study is conducted among current or recent customers and is used to ascertain the customer experience for a specific transaction or interaction. This type of research looks at near or short-term evaluations of the customer experience and often focuses on operational metrics.
In contrast, the relational or relationship customer experience study is typically conducted among a random sample of the company’s customer base. Relational customer experience is used to understand the cumulative impressions customers form about their entire customer experience with the company. Importantly, this type of customer experience research is often the chassis for ascertaining specific aspects of the experience important to predicting loyalty and other customer behaviors.
A. Transactional Customer Experience
In a transactional customer experience study, we focus on the details of a customer’s specific recent transaction. For example:
- The respondent’s most recent visit to Wendy’s
- The customer’s visit yesterday to her local Deutsche Bank branch
- Last week’s call to the Blue Cross/Blue Shield customer service center
- The respondent’s visit, 10 days ago, to Nielsen Nissan in Chesterton, Indiana, for routine auto maintenance.
The overall rating we ask is the respondent’s overall evaluation of the specific transaction (visit, stay, purchase, and service). The attribute ratings are also specific to the specific transaction.
B. Relational Customer Experience
A relational customer experience study is broader in coverage. Here, we ask about the totality of the relationship with a company. In a relational customer experience study, the questions relate to the overall, accumulated experience the customer has had with the company. So rather than ask about the timeliness of an oil change at Nielsen Nissan and the quality of that service, the relational survey would ask for the respondent’s overall perceptions of Nielsen Nissan’s services across all the times the customer has interacted with that dealership.
The overall ratings are often overall satisfaction with the relationship as a whole, willingness to recommend, and likelihood to return. Attributes are similarly broader in scope. We would not ask the customer about her satisfaction with the speed of service for her last oil change, instead we would ask about her satisfaction with the speed of service she usually gets when she visits Nielsen Nissan.
C. Sampling Differences Between Transactional and Relationship Studies
In addition to the content of the surveys, a critical difference between these two studies is the sampling frame. In a transactional customer experience study, we sample customers who have interacted with the company recently. This is also sometimes called “trigger-based” customer experience since any type of interaction with the company can “trigger” the inclusion in a transactional customer experience study.
In a relational customer experience study, we typically sample from the entire base of customers, including people who may not have interacted with the company recently. A relational customer experience study is projectable to the entire customer base, while a transactional customer experience study is a sub-set of customers – those who have interacted recently.
When leveraging customer experience information with internal information, transactional customer experience information is often linked to operational metrics (such as wait time, hold time, staffing levels, etc.). In turn, through the use of bridge modeling, transactional research is often linked to relational customer experience, which is then linked to downstream business measures, such as revenue, profitability and shareholder value-add.
D. Recommendations for Relationship Surveys
Survey Content: As mentioned above, relationship surveys are meant to measure the totality of customers’ experiences with a given company. They are also meant to determine how customers are feeling about the company NOW. It is important to note that customers overall feelings about a company (as measured in relationship surveys) are often NOT the average of their transactional experience evaluations. This is because different transactions, especially if they are negative, can have a much larger effect on overall feelings toward a company than other transactions.
Most relationship surveys contain questions addressing:
- Overall Metrics such as Likelihood to Recommend the Company, Overall Satisfaction with the Company, and Likelihood to Return or Repurchase
- High-level brand perceptions
- Company service channels usage and evaluations such as store/ dealership, finance company, call center/problem resolution teams, etc.
- Product usage and evaluations
- Share of Wallet measures
- Marketing/communication perceptions
Survey Sampling: Who, how often and how many customers do you need to survey? There are no hard and fast rules but remember the idea is to obtain a representative sample of your customers. With that in mind:
Who to Survey: All customers (whether they are recently active or not) should be available for sampling. You also might want to oversample small but important groups of customers (e.g., millennials, new owners, etc.) to ensure that you receive enough returns to analyze these groups separately. However, if you do oversample you will need to weight your data back to your customer demographics to ensure representative overall results.
How Often to Survey: While transactional CX research is usually done on a continuous basis, relationship studies are usually conducted once or twice per year. How often companies conduct relationship studies is usually determined by the number of customers available (i.e., are there enough to conduct the study twice per year?) and when and how often decisions will be made based on the findings.
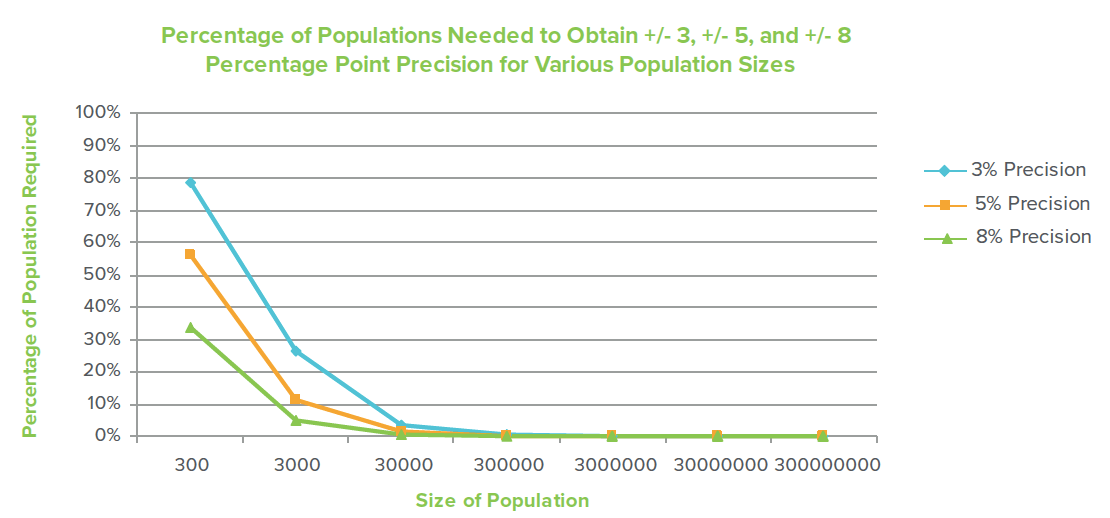
How Many to Survey: This is often the most frequent question clients ask and the basic answer is that it depends on what organizational level you need the results to be representative of. The good news is that if you are only concerned about making decisions on the entire company level, only about 1000 well-sampled responses is sufficient. For most large companies that is a very small percentage of their customers. However, if you want the finding to be representative of lower levels of the organization for comparison purposes (e.g., zones, districts, stores) or want findings to be representative of certain customer groups (e.g., millennials, minorities, long-term customers, etc.) calculations need to be performed to determine the number of responses needed for these groups. Unfortunately, as demonstrated in the chart below, as the population size (e.g., company customers, zone customers, store customers) goes down, the percentage of customers needed to represent that population goes up. For instance, to obtain +/- 3 percentage point precision for a population of 3,000,000 people you only need 1067 randomly sampled returns. That is just 0.04% of the population. For a population of 30,000 people, you need 1030 returns which is 3.4% of the population. For a population of 3,000 the number of returns needed drops to 787, but that is 26.2% of a population of 3,000. For a very small population like 300, you need returns from 234 people (78.0%) of the population.
E. Summary
Both transactional and relationship surveys are key parts of any comprehensive customer experience program. Transactional surveys are great for assessing the quality of specific customer touch points and making improvements in those areas. Relationship surveys allow for the assessment of the entire customer experience across all touchpoints and therefore more closely relate to customer behaviors such as loyalty, customer spend, and customer advocacy.