Three Ways a CX Mindset can Power Your Loyalty Marketing Program
Though loyalty marketing programs and customer experience both have similar goals, it is vital that marketers recognize customer experience goes beyond the membership/incentive mindset. When you focus on customer experience, you can enrich all areas of your business
In my last post, I discussed the expanding role of the CMO from steward of the brand to caretaker of the end-to-end customer relationship. While this transition has been recognized by various studies, it has been especially evident in my own experience as Chief Marketing Officer at InMoment. In fact, my position gives me an even more interesting and unique perspective: I have a front row seat to new developments in the marketing world and to the evolution of the customer experience (CX) industry.
Today’s marketers are increasingly seeing customer experience fall under their umbrella of duties, and it’s easy to confuse CX efforts with traditional marketing approaches such as loyalty marketing programs. However, marketers should be warned that this is a place where “similar” definitely does not mean “equal.”
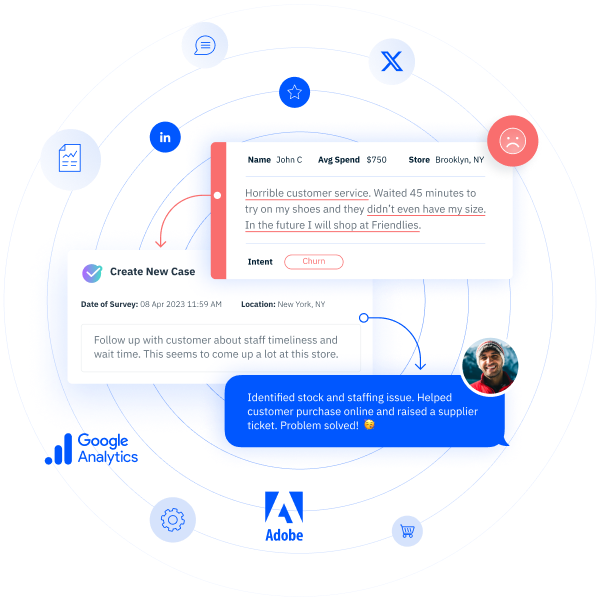
Loyalty marketing programs refer to a company-wide initiative that is focused on growing and retaining existing customers by selling them more. CX programs help businesses understand the customer/brand relationship and what makes the customer loyal to the brand in the first place. The key difference between the two is in their approach: loyalty marketing is selling—often through incentives—while customer experience focuses on the ongoing conversation with the customer to then drive a deeper sense of loyalty.
This is where a traditional approach to loyalty programs goes wrong: At the end of the day, your customers don’t want to be bought with coupons, infrequent freebies, and discounts. While they appreciate them, they aren’t what makes them loyal. Customers want to feel valued and heard. If you look through the lens of customer experience, you can reset your loyalty marketing programs to take a more holistic, relationship-centric approach that will truly impress your customers.
Here are three specific ways a CX mindset can help you take your loyalty program to the next level:
Craft a Consistent Experience
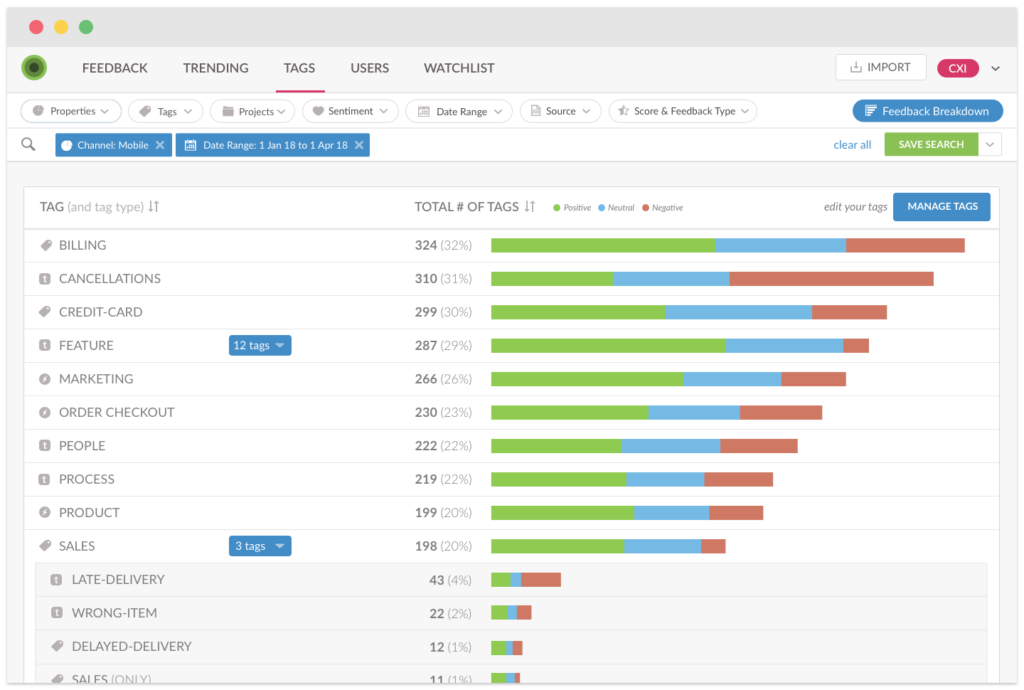
Each year, InMoment surveys both brands and customers to unearth the latest trends in customer experience. The 2018 CX Trends Report revealed that consumers across all industries are creeped out by the way companies use their personal data and are therefore more reluctant to share that data. This can be a massive problem for loyalty marketing programs as they require customers to enroll by sharing some form of personal data. So how can a CX mindset help you solve this possible customer objection? One word: consistency.
Customers need to know that they can trust your brand from the get-go. If they’re receiving mixed messages in policy, employee interaction, or overall experience, they aren’t going to know what to expect and will be less likely to trust you with their information. If you approach this problem with a CX mindset, you know that you need to dedicate resources to unearth areas of brand inconsistency so you can streamline, hire, and train appropriately and put the best foot forward before asking for customer data.
If customers have a great impression of who you are as a brand, their positive and consistent experiences will inspire the trust they need to join your loyalty program.
Provide the Right Perks
Though perks alone won’t drive true brand loyalty, they are incredibly necessary to provide what customers expect when they sign up. However, your efforts can be all for nought if you aren’t providing the right incentives.
According to that same CX Trends report, customers are less likely to share their info when a program simply offers to make interactions easier, more efficient, or to deliver personalized recommendations. What they do value is when they receive exclusive access to sales, events, or products. Essentially, today’s customers are more willing share their data if they are given the VIP treatment.
The listening capabilities of a CX platform can help you to further narrow down what perks really drive participation in your loyalty programs.
Focus on Relationships, Not Memberships
Sure, customer satisfaction is a short-term win. After all, if a customer was able to purchase the product or service they were looking for, they might be more willing to become a loyalty program member. But why stop there? When you provide excellent brand interactions over and over again, you have a customer that will come back, buy more, and recommend you to others. That is the kind of customer you create when you focus on relationships and loyalty over merely satisfaction.
The key to going beyond “good” and creating excellent experiences is emotion. When InMoment studied unstructured customer data, we found that when discussing memorable experiences, most customers concentrated on the interactions they had with brand representatives and, even more importantly, the emotions they evoked. Ultimately, it’s not the 20% off coupons that inspire emotional experiences, it’s the meaningful human interactions that keep customers around in the long run.
With customer experience, you can go beyond collecting loyalty members and utilize emotion to create lasting impact.
Though loyalty marketing programs and customer experience both have similar goals, it is vital that marketers recognize customer experience goes beyond the membership/incentive mindset. When you focus on customer experience, you can enrich all areas of your business—including your loyalty program—by understanding your customers, evoking positive emotions, and fostering long-lasting relationships.
To learn more about what customers expect from their brand interactions, check out the 2018 CX Trends Report: What Brands Should Know About Creating Memorable Experiences!