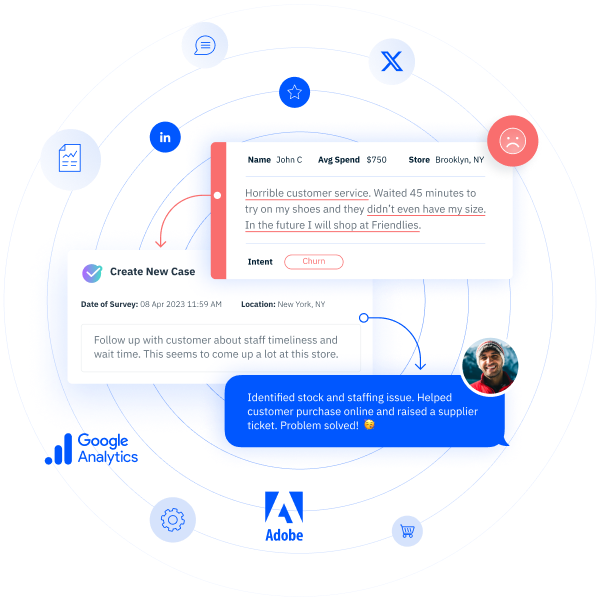
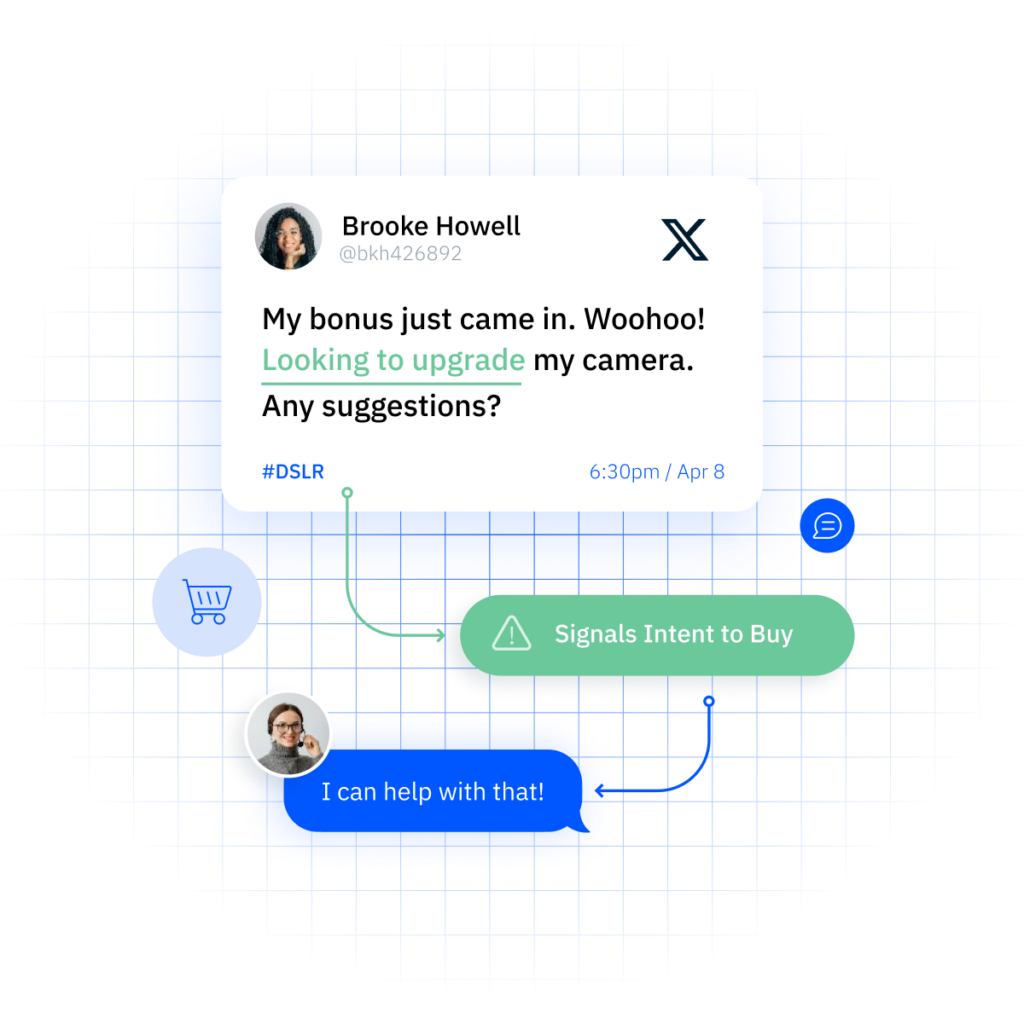
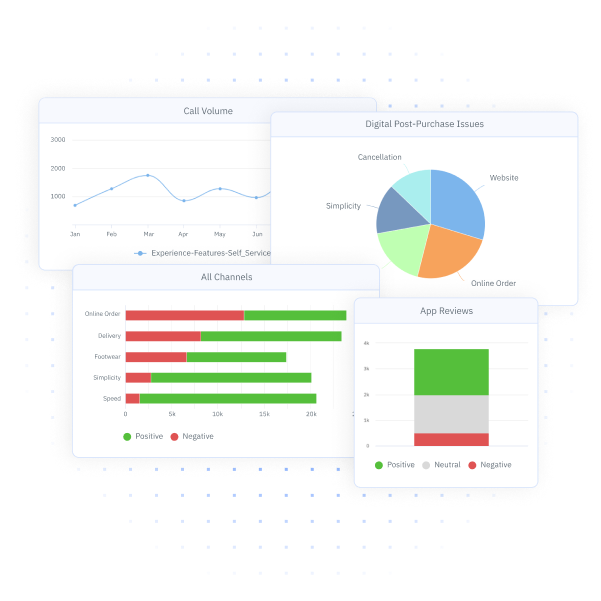
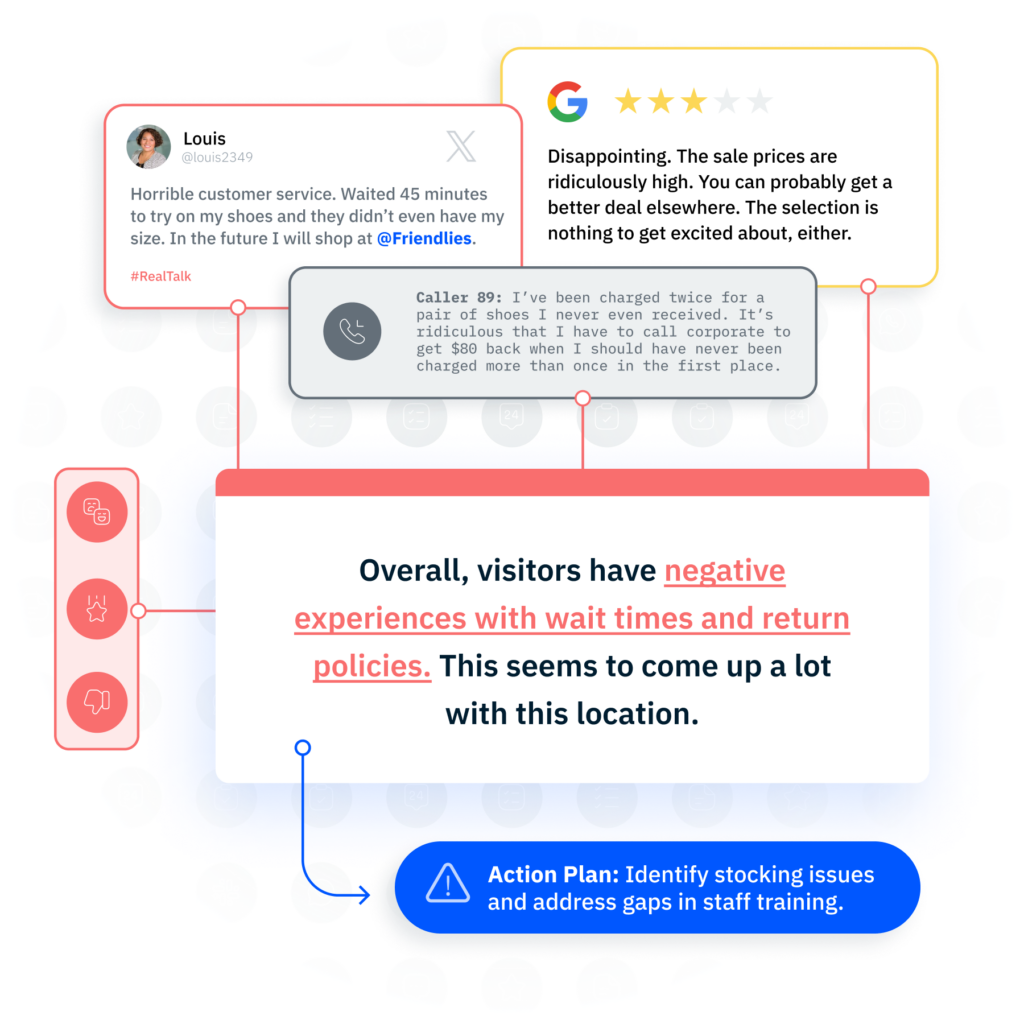
Customer experience doesn’t break in one place. It slips—moment by moment—until the customer quietly walks away. The missed cue in a contact center call. The unacknowledged product review. The digital journey that stalls just before conversion. These aren’t one-off issues. They’re customer signals, and they’re telling you something important.
The problem is most businesses aren’t listening closely enough. Research shows that up to 85% of valuable customer data is sitting idle—trapped in silos, disconnected from the journey, or never analyzed at all. That’s not just a data problem. It’s a growth problem.
High-performing CX teams understand that every customer interaction—whether it’s behavioral, emotional, or transactional—offers insight into what’s working and where things need to change. The ability to capture, connect, and act on these signals is what separates reactive service from CX programs that drives real business outcomes.
What Are Customer Signals?
Customer signals are the clearest indicators of how someone is experiencing your brand. They’re embedded in every click, comment, conversation, and conversion. When decoded properly, these signals help organizations anticipate needs, close gaps, and deliver experiences that build trust and long-term value.
There are three core types of customer signals:
- Behavioral signals reflect what people do. Actions like clicking on a help article, abandoning a cart, or hesitating at a key moment in the onboarding flow can tell you volumes about intent and friction points.
- Emotional signals highlight how customers feel. These show up in post-interaction surveys, online reviews, call transcripts, or even the absence of feedback altogether.
- Transactional signals capture what has already happened—purchases, returns, renewals, cancellations—and offer measurable clues about satisfaction or risk.
Relying on just one type of signal won’t cut it. A five-star rating doesn’t explain why a customer almost didn’t buy. A drop in conversions doesn’t reveal what emotion was behind the decision. It’s the full picture—structured and unstructured data, gathered across journeys—that unlocks the richest insight.
When organizations combine these signals within an integrated CX strategy, they shift from reacting to problems to proactively designing better experiences. That’s how you own the moments that matter.
Why Customer Signals Matter in CX
Customer signals don’t just reflect experience—they shape it. When businesses capture and analyze the right mix of signals across every channel, they can spot patterns, predict behavior, and intervene before issues escalate. Instead of reacting to problems after the fact, CX teams can influence the journey in real time and deliver outcomes that stick.
Signals fuel CX programs by giving teams the clarity to act where it matters most—whether that’s saving a customer from churn, personalizing support, or informing a company-wide shift in strategy. When used well, they become the foundation for customer experience that’s both responsive and resilient.
Provide Insight Into Customer Needs and Expectations
Today’s customers don’t always tell you what they want, but their behavior does. By continuously monitoring signals like digital activity, service inquiries, and review trends, CX teams can see preferences shift as they happen. This real-time insight helps organizations stay ahead of evolving expectations and fine-tune experiences without relying solely on lagging survey data.
Rather than guess what customers value, teams can spot patterns that point to new needs—then move quickly to meet them. Whether it’s adapting onboarding flows, refining support journeys, or launching new features, customer signals are the early indicators of what’s next.
Help Identify Churn Risks or Dissatisfaction Early
Every silent unsubscribe, dropped renewal, or unanswered survey is a missed opportunity to intervene. But the warning signs are often there—buried in review sentiment, support call frustration, or reduced digital engagement.
By analyzing these early signals, businesses can pinpoint at-risk customers before they walk away. Declining usage, rising effort, or a sudden spike in negative feedback all serve as red flags. When teams are equipped to spot these indicators, they can step in with meaningful action—resolving friction, restoring trust, and protecting revenue.
Enable More Personalized, Timely Responses
Generic service doesn’t cut it anymore. Customers expect support that understands their history, preferences, and intent. Customer signals make that possible.
By connecting structured data (like purchase history or ticket volume) with unstructured signals (like sentiment in a support chat or context from a product review), brands can respond with precision. A contact center agent sees not just the current issue, but the emotional tone behind it. A marketing team tailors messages based on real-time behavior, not just segments.
Personalized, context-aware interactions increase satisfaction and reduce effort—especially at scale.
Improve Decision-Making Across Product, Support, and Marketing
When customer signals are connected and analyzed holistically, they do more than inform daily service—they drive business strategy. Teams gain clarity on what’s resonating, what’s breaking, and where to focus next.
Aggregated signal data reveals trends that single-source metrics miss. That includes what customers are saying, doing, and feeling across journeys—bringing together structured inputs (like survey results or CSAT) with unstructured insights (like open-ended feedback, reviews, or chat transcripts).
This eliminates the guesswork from decision-making. Product teams prioritize the features customers care about. Support leaders optimize staffing based on emotional tone, not just ticket volume. Marketing targets the right audience at the right moment.
Signal-driven strategy creates alignment across departments and turns the voice of the customer into a shared, actionable asset
The Types of Customer Signals
Customer signals come from more places than most teams realize. They’re scattered across digital journeys, service channels, reviews, systems, and even internal operations. When captured in isolation, these signals offer a partial view. But when unified, they form a powerful lens into what customers need—and how businesses should respond.
To build a truly integrated customer experience, organizations must bring together a variety of signal types, including behavioral patterns, emotional cues, demographic insights, direct and indirect feedback, and operational data. Here’s how each contributes to the full picture.
Behavioral Signals
These are the digital footprints customers leave behind—subtle but telling patterns in how they navigate your products, platforms, or spaces. Click-through rates, session lengths, cart abandonment, repeat purchases, feature usage, and login frequency all signal where attention is going—and where friction might exist.
Behavioral data helps CX, product, and marketing teams understand intent. Is a customer ready to buy? Losing interest? Exploring a new use case? Recognizing these signals early allows teams to tailor experiences that increase relevance and reduce drop-off.
Emotional Signals
Customer interactions are rich with emotional context—if you know how to look for it. Emotional signals are embedded in tone of voice, language choices, and the intensity or urgency of a message. They show up in support calls, surveys, social posts, and even in silence.
Beyond just mood, these signals often reveal intent and effort. For example, frustration in a review may reflect a high-effort experience. Warm language in a support ticket can indicate loyalty. When analyzed properly, emotional signals guide better conversations, more empathetic service, and smarter resource prioritization.
This is also where Conversational Intelligence shines—uncovering emotion, effort, and intent at scale across voice and text interactions.
Demographic Signals
Context matters, and demographic signals provide it. Details like age, geography, industry, job title, and company size help anchor customer behavior in something concrete. This enables teams to understand patterns at a deeper level and tailor experiences accordingly.
A churn risk in one region might not apply to another. A friction point for retail customers could look very different in financial services. Demographic context ensures that personalization efforts aren’t just data-driven—they’re meaningful.
Feedback Signals
Not all feedback is created equal. To capture the full story, organizations need to listen in both direct and indirect ways:
- Direct feedback includes structured inputs like post-purchase surveys, Net Promoter Score (NPS) data, review ratings, support ticket comments, and contact center conversations. These offer explicit insight into satisfaction, expectations, and perceived value.
- Indirect feedback shows up in the wild—social media threads, unsolicited online reviews, third-party forums, and beyond. This unfiltered input is often more candid, making it a valuable source of real sentiment and emerging trends.
Listening to both feedback types—especially when layered with other signals—makes it easier to identify what customers are saying, how they’re saying it, and what needs attention.
Operational Signals
Some of the most overlooked signals are already sitting inside your systems. CRM entries, case notes, transaction logs, agent performance data, fulfillment delays, and even call routing paths—all fall into the operational category.
These signals reflect what’s happening behind the scenes and offer crucial insight into experience delivery. For example, repeat contact on a single issue may reveal a broken process. A spike in call volume tied to a specific product suggests deeper support needs.
Bringing operational signals into the CX ecosystem connects front-stage experiences with back-stage performance and helps teams align process improvements with actual customer impact.
How Customer Signals Enhance the Customer Experience
Customer signals are more than scattered data points, they’re powerful tools for transformation. When organizations connect the dots across structured feedback, digital behavior, sentiment, and operational systems, they gain the ability to move from fragmented insights to coordinated action.
This unified view allows teams to personalize outreach, anticipate needs, identify risks early, and continuously improve experiences in ways that directly impact retention, revenue, and brand perception.
1. Create a Holistic View of Customer Experience
The first step toward experience transformation is seeing the full picture. Isolated feedback channels can’t provide it. But when organizations integrate signals across systems, teams, and journeys, they start to uncover how experiences truly unfold—and where they fall apart.
A holistic view of customer experience combines operational signals (like call logs and CRM notes), feedback signals (from surveys or reviews), and emotional indicators (like sentiment or effort) into one shared source of truth. That kind of visibility doesn’t just support better strategy—it drives immediate action.
Recurring complaints might point to a product quality issue. Surging call volumes could flag gaps in onboarding or documentation. Patterns in frontline interactions may reveal the need for updated training. With signal intelligence shared across the business, every department—from product to people ops—can respond with speed and clarity.
2. Facilitate Targeted Audience Engagement
Modern CX isn’t about blasting the same message to every customer. It’s about delivering the right message, at the right moment, to the right audience.
Customer signals make that possible. By analyzing behavior, sentiment, and preferences, brands can move from static segmentation to dynamic audience targeting—sending relevant offers or content based on real-time context.
But the opportunity doesn’t stop at segmentation. Integrated CX leaders go further, using individualized data to tailor messages to the person, not just the persona. A customer browsing pricing pages gets a personalized support message. A returning guest receives recommendations aligned to past stays or purchases.
When signals guide outreach, engagement becomes more than timely—it becomes meaningful.
3. Anticipate Customer Needs Before They’re Expressed
Customer signals offer predictive power. By mapping patterns across feedback, usage data, and operational trends, teams can proactively address friction before it becomes a problem.
This means fewer support tickets, faster resolutions, and less customer effort. It also means smarter product recommendations, better onboarding journeys, and perfectly timed check-ins that feel intuitive, not invasive.
Predictive insights fueled by real signals allow brands to stay one step ahead, meeting customer needs before they’re spoken aloud.
4. Identify and Address Dissatisfaction Early
Not all customers complain. Many simply disengage. That’s why the ability to detect dissatisfaction early is one of the most valuable use cases for customer signals.
Changes in sentiment, tone, or behavior often appear well before a customer cancels or churns. By decoding emotional and behavioral cues, businesses can surface root causes—whether that’s a product issue, service breakdown, or misaligned expectation.
And it’s not just about identifying problems. It’s about acting on them. Insights-driven actions are what turn a risk into a recovery. A follow-up message. A proactive refund. A priority ticket escalated without the customer needing to ask.
This kind of responsiveness builds loyalty. Even after a bad moment.
5. Enhance Agent Coaching and Support
Customer signals don’t just guide strategy—they also shape day-to-day performance. In contact centers, signals offer a real-time window into how agents are delivering experiences and where support is needed.
Instead of relying on random call sampling or outdated scorecards, CX leaders can monitor emotional tone, hold time, resolution speed, and feedback accuracy to build targeted coaching programs. This allows frontline leaders to personalize coaching and close skill gaps quickly.
The result is better agent confidence, improved consistency, and higher satisfaction for both teams and customers.
6. Benchmark Against Competitors
To lead the market, you need to know how you measure up. Aggregated signal data—across reviews, surveys, call center sentiment, and behavioral trends—can help benchmark performance against competitors in real time.
Customer signals make it possible to compare key metrics like Net Promoter Score, average star ratings, or churn indicators by region, product, or service line. This competitive insight helps CX leaders prioritize investments, fine-tune brand messaging, and capitalize on opportunities to differentiate.
7. Drive Innovation With Crowd-Sourced Ideas From Customer Feedback
Innovation doesn’t start in the boardroom—it starts with customers. Open-text feedback, unsolicited reviews, and even product complaints are rich sources of new ideas.
When organizations treat these signals as more than noise, they unlock an engine for continuous improvement. Teams can spot emerging trends, identify feature requests, and prioritize changes that reflect real demand.
It’s insight-led innovation, grounded in what customers actually want—and powered by the signals they’ve already given you.
Turn Customer Signals Into CX Insights With InMoment
Customer signals are everywhere, but most organizations are only hearing part of the story. To create exceptional experiences, businesses need more than surveys or analytics dashboards. They need to connect every signal—across every channel, every moment, and every team—and turn those inputs into action.
That’s exactly what InMoment helps enterprise brands do. Our Integrated CX platform unifies feedback, sentiment, behavioral data, and operational signals into a single, powerful system of intelligence. With advanced analytics, Conversational Intelligence, and deep industry expertise, we help you see the full picture and act where it counts.
Whether you’re looking to reduce churn, improve frontline performance, or drive growth through better insights—start by listening smarter.